In spontaneously breathing tracheostomy patients who require oxygen flow rates of less than 4 LPM there are two options available: Note: HME are used without a heated humidifier circuit.



Journal of Pediatrics 156:634-38, Spentzas, T., Minarik, M., Patters, AB., Vinson, B. and Stidham, G. (2009) Children with respiratory distress treated with high-flow nasal cannula. (7th ed.).

Oxygen is a drug and should be prescribed with a target saturation range. Check nares for patency - clear with suction as required.
Where oxygen weaning is successful, continuous pulse oximetry monitoring may be discontinued. Isolette use in paediatric wards, RCH internal link only. Due to this the following rules should be followed: Oxygen cylinders should be secured safely to avoid injury. It allows the oxygen therapy to continue during feeding/eating and the re-breathing of CO2 isn't a potential complication. Please consult user manuals for any other models in use. Frey, B., & Shann, F. (2003).
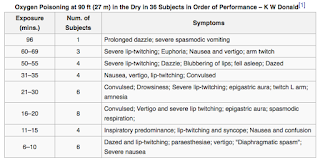
Additionally in some conditions (eg. Normal values and SpO 2 targets, Appendix A - Paediatric sizing guides for nasal prongs. The treatment of an acute or emergency situation where hypoxaemia or hypoxia is suspected, and if the child is in respiratory distress manifested by: use of accessory muscles: nasal flaring, intercostal or sternal recession, tracheal tug, Short term therapy e.g. To ensure the highest concentration of oxygen is delivered to the patient the reservoir bag needs to be inflated prior to placing on the patients face. Thank you for your interest in spreading the word on European Respiratory Society . HFNP nursing clinical guideline for more information. asthma, bronchiolitis, and pneumonia) and can be managed with SpO, Oxygen therapy should be closely monitored & assessed at regular intervals, Children with cyanotic congenital heart disease normally have SpO. 24(5): 323-8, Miyamoto, K. & Nishimura, M. Nasal Dryness Discomfit in Individuals Receiving Dry Oxygen via Nasal cannula Respiratory Care April (2008) Vol 35 No. Use of oxygen in continuous positive airway pressure ventilation systems, heliox and nitrous oxide mixtures, procedures that require conscious sedation, the peri-operative period and in track and trigger warning systems (e.g. O'Driscoll was paid an honorarium, by the ERS, for delivering a lecture on Emergency Oxygen Therapy at the ERS meeting in Vienna 2009.

Why is a guideline for emergency oxygen necessary? This question is for testing whether or not you are a human visitor and to prevent automated spam submissions. A non-rebreathing face mask has an oxygen reservoir bag and one-way valve system which prevents exhaled gases mixing with fresh gas flow. As with the other delivery systems the inspired FiO2 depends on the flow rate of oxygen and varies according to the patient's minute ventilation.

Oxygen therapy should be reduced or ceased if: This direction applies to patients treated with: See below nursing guidelines for additional guidance in assessment and monitoring: Unless clinically contraindicated, an attempt to wean oxygen therapy should be attempted at least once per shift. The FiO2 inspired will vary depending on the patient's inspiratory flow, mask fit/size and patient's respiratory rate. The
Oxygen is indicated in a patient who is suffering an acute MI who has saturation of 90%. Online ISSN: 2073-4735, Copyright 2022 by the European Respiratory Society. Only patients with COPD are at risk of T2RF. Emergency oxygen therapy: from guideline to implementation, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, University of Manchester, Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Salford Royal Foundation NHS Trust, Both authors contributed equally to this article, Audit of oxygen use in emergency ambulances and in a hospital emergency department, British Thoracic Society emergency oxygen audits, Short burst oxygen therapy in patients with COPD, BTS guideline for emergency oxygen use in adult patients, Effects of supplemental oxygen administration on coronary blood flow in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization, Systematic review of studies of the effect of hyperoxia on coronary blood flow, Postischemic reperfusion injury can be attenuated by oxygen tension control, Should stroke victims routinely receive supplemental oxygen? Patients who require an FiO2 greater than 50% require PICU medical review. Frequently Asked Questions. Position the tubing over the ears and secure behind the patients head.

Start 24 or 28% oxygen via a Venturi mask, then check blood gases. No difference was found between the two arms of the study in 30 day mortality or infarct size. Archives of Disease in Childhood. June, Vol.97, Issue 9, pg827-830, Ricard, J. Updated July 2017. Below is an image of the RT330 pressure relief valve. Simple nasal prongs are available in different sizes. Oxygen (via intact upper airway) via a simple face mask at flow rates of 4LPM does not routinely require humidification. Non-rebreathing face mask are not designed to allow added humidification. The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients not at risk of type II respiratory failure is 9498%.


Oxygen is a drug and should be prescribed. The humidifier should always be placed at a level below the patient's head. Nippers, I., & Sutton, A. Part I. European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, the ACCP and the SCCM, Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, The incidence and effect on outcome of hypoxemia in hospitalized medical patients, Reliability of pulse oximetry in titrating supplemental oxygen therapy in ventilator-dependent patients, Relationship between supranormal oxygen tension and outcome after resuscitation from cardiac arrest, The effect of supplemental oxygen on hypercapnia in subjects with obesity-associated hypoventilation: a randomized, crossover, clinical study, Randomised controlled trial of high concentration, Randomized controlled trial of high concentration oxygen in suspected community-acquired pneumonia, A randomized controlled trial of oxygen therapy in acute myocardial infarction Air Verses Oxygen In myocarDial infarction study (AVOID Study), A clinicians review of the respiratory microbiome, www.nrls.npsa.nhs.uk/resources/?entryid45=62811. ), Appendix A - Pediatric sizing guides for nasal prongs, Fisher and Paykel Optiflow junior range sizing guide. The child should appear clinically well. Respiratory Distress (work of breathing) should be mild, or there should be no work of breathing. The image below is of the RT330 circuit. 20 (6), 39-45. B.R.


Bersten, A. D. & Soni, N. (2013). 91 - 95% for premature and term neonates (, 90% for infants with bronchiolitis (link to, The treatment of documented hypoxia/hypoxaemia as determined by SpO, Achieving targeted percentage of oxygen saturation (as per normal values unless a different target range is specified on the observation chart.).

Oxygen is a treatment for hypoxaemia not breathlessness.

This system is useful in accurately delivering concentrations of oxygen (21 95%). Optiflow Nasal Prong junior and standard humidification and flow rate guide for Airvo. Humidification can be provided using either the MR850 Humidifier or the AIRVO 2 Humidifier. < 40 cm H20. Has two modes: Follow instructions in the
Level of consciousness (LOC) = alert, colour = pink, behaviour = normal. Sydney, Australia: Brink, F; T Duke, T., Evans, J. The minimum flow rate through any face mask or tracheostomy mask is 4 LPM as this prevents the possibility of CO2 accumulation and CO2 re-breathing. An orange traffic light confirms the AIRVO 2 has not been cleaned and disinfected since last use, and is not safe for use on a new patient. Humidification during oxygen therapy and non-invasive ventilation: do we need some and how much? Select a mask which best fits from the child's bridge of nose to the cleft of jaw, and adjust the nose clip and head strap to secure in place. Therefore, the results only apply to the short period of time between admission to hospital and primary PCI. Implementing the Rapid Response Report Oxygen Safety in Hospitals. Clinical assessment and documentation including but not limited to: cardiovascular, respiratory and neurological systems should be done at the commencement of each shift and with any change in patient condition. November, Vol.134, No.5, pge1474-e1502, Ramsey, K. (2012). The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients at risk of type II respiratory failure is 8892%. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier, Nagakumar, P. Doull, I. All high flow systems require humidification. Maintain efficient and economical use of oxygen. Non-Invasive Mode delivers gas at a comfortable level of humidity (31-36 degrees, >10mg/L). The Hudson Trach-Vent HME has a dead space of 10mL and is recommended for use in patients who have tidal volumes of 50mL and above. Oxygen delivery method selected depends on: Note: Oxygen therapy should not be delayed in the treatment of life threatening hypoxia. Where the Airvo2 is used as an oxygen delivery device the flow from this device is independent to the flow of oxygen. On arrival his oxygen saturation is 82% on room air, the correct course of action is: Do not give oxygen until blood gas results are available. Do nothing, he is known to have COPD and is often breathless and anxious. Trach-Vent's are changed daily or as required if contaminated or blocked by secretions. St. Clair, N., Touch, S. M., & Greenspan, S. (2001). For nasal prong oxygen withhumidification a maximum flow of: Optiflow nasal prongs are compatible for use in humidified low or high flow oxygen delivery. asthma, the hyperventilation of dry gases can compound bronchoconstriction. Clinical observations:

See guide below for recommended patient sizing and flow rates. < 90% for infants with bronchiolitis, The child with cyanotic heart disease reaches their baseline Sp0, Mechanical ventilation (do not alter other ventilator settings), Mask-BiPaP or CPAP (do not alter pressure or volume settings. Position the nasal prongs along the patients cheek and secure the nasal prongs on the patients face with adhesive tape. The next version of the BTS emergency oxygen guideline will be titled: BTS guideline for oxygen use in adults in healthcare and emergency settings and there will be a separate guideline on emergency use in children. Oxygen is not a flammable gas but it does support combustion (rapid burning). The pressure relief valve has been set to a limit of
Appendix A for further information regarding appropriate junior range sizing: Fisher and Paykel Optiflow junior range sizing guide, Fisher and Paykel Optiflow nasal cannula standard range, (
Schibler, A., Pham, T.,Dunster, K., Foster, K., Barlow, A., Gibbons, K., and Hough, J. (2014). If you require further information please click here for the
Medical gases, including air and oxygen, have a drying effect on mucous membranes resulting in airway damage. Therefore, humidification of nasal prong oxygen therapy is recommended. Enter multiple addresses on separate lines or separate them with commas. Intensive Care Med (2009) 35: 963-965. Check and document oxygen equipment set up at the commencement of each shift and with any change in patient condition.

This study will enrol 490 patients and includes controlled oxygen therapy in the pre-hospital setting [34].

Evidence-Based Protocols to Guide Pulse Oximetry and Oxygen Weaning in Inpatient Children with Asthma and Bronchiolitis: A Pilot Project. Oxygen should be given to all patients having an acute stroke regardless of oxygen saturation. Follow the manufacturers Instructions for use for each device and setup.

Secretions can become thick & difficult to clear or cause airway obstruction. (
Oxygen therapy and oxygen delivery principles (respiratory therapy). RCH predominantly uses the Fisher & Paykel MR850 Humidifier & AIRVO 2 Humidifier. The main safety feature of the RT330 Oxygen Therapy System is the pressure relief valve. Considerations when using a non-rebreathing face mask.
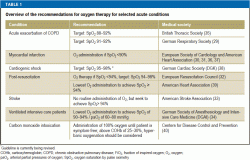
For most patients with COPD, target saturation range should be set at 8892% until blood gases are available. Neonatal Network. Supplemental oxygen relieves hypoxaemia but does not improve ventilation or treat the underlying cause of the hypoxaemia. The type of humidification device selected will depend on the oxygen delivery system in use, and the patient's requirements. Note: Some flow meters may deliver greater than the maximum flow indicated on the flow meter if the ball is set above the highest amount. A range of flow meters are available at RCH, 0-1 LPM, 0-2.5 LPM, 0-15 LPM. Publication is anticipated in 2014.


A patient with COPD and a history of hypercapnic respiratory failure becomes very breathless on the ward. Invasive Mode - delivers saturated gas as close to body temperature (37 degrees, 44mg/L) as possible. centre or top of ball), or dial (Perflow brand of flow meters) when setting the flow rate. In some conditions e.g. use of accessory muscles/nasal flaring - see Respiratory Distress on EMR), Ensure the individual MET criteria are observed regardless of oxygen requirements, Cease oxygen therapy entirely and maintain line of sight for approximately 5 minutes, LOC = alert, note lethargy or irritability, Non re-breather face mask (mask with oxygen reservoir bag and one-way valves which aims to prevent/reduce room air entrainment), Isolette - neonates (usually for use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit only), Face mask or tracheostomy mask used in conjunction with an, NB: There is separate CPG for HFNP use in the NICU (see, Cold, dry air increases heat and fluid loss.

Any patient who does not exhibit signs of clinical stabilization with 4 hours of commencement of HFNP should be considered for transfer to the PICU. Has two modes: Link to : Optiflow Nasal Prong Flow Rate Guide. NB: The above values are generalized to the paediatric population, for age/patient specific ranges please consult the covering medical team. Which of the following statements are true? Feeding adequate amounts orally. (See
For all critically ill patients, high concentration oxygen should be administered immediately until the patient is stable.

Mosby's Skills.
Which of the following statements regarding oxygen prescribing are true? To ensure the patient is able to entrain room air around the nasal prongs and a complete seal is not created the prong size should be approximately half the diameter of the nares. Ralston, S.L., Lieberthal, A.S., Meissner, H.C., Alverston, B.K., Baley, J.E., Gadomski, A.M., Johnson, D.W., Light, M.J., Maraqa, n.F., Mendonca, E.A., Phelan, K.J., Zorc, J.J., Stanko-Lopp, D., Brown, M.A., Nathanson, I., Rosenblum, E., Sayles III, S. & Hernandez-Cancio, S. (2014) Pediatrics. Check nasal prong and tubing for patency, kinks or twists at any point in the tubing and clear or change prongs if necessary. (2014). However, if humidification is clinically indicated - set up as per the recommended guidelines for the specific equipment used. & Boyer, A. This study was flawed in that patients were randomised to treatment in hospital and most had received high-flow oxygen in the ambulance en route to hospital. Care and considerations of child with simple nasal prongs: If the required flow rate exceeds those as recommended above this may result in nasal discomfort and irritation of the mucous membranes. The aim of this guideline is to describe the indications and procedure for the use of oxygen therapy, and its modes of delivery. Oxygen administration in infants. May, Vol 50 (5) pp373-378, McKieman, C., Chua, L.C., Visintainer, P. and Allen, P. (2010) High Flow Nasal Cannulae Therapy in Infants with Bronchiolitis. The goal of oxygen delivery is to maintain targeted SpO2 levels in children through the provision of supplemental oxygen in a safe and effective way which is tolerated by infants and children to: Should an aerosol generating procedure be undertaken on a patient under droplet precautions then increase to airborne precautions by donning N95/P2 mask for at least the duration of the procedure. Follow the instructions in the disinfection kit manual: For routine cleaning instructions please refer to the following link:
The above values are expected target ranges. NOTE: We only request your email address so that the person you are recommending the page to knows that you wanted them to see it, and that it is not junk mail. (2012) Current Therapies for Bronchiolitis. We do not capture any email address. TRACH-VENT+: Alternatively a Hudson RCI HME - TRACH-VENT+ has an integrated oxygen side port which connects directly to oxygen tubing which is attached to the oxygen source (flow meter). Hourly checks should be made for the following: Hourly checks should be made and recorded on the patient observation chart for the following (unless otherwise directed by the treating medical team): respiratory distress (descriptive assessment - i.e. RT330 circuit - click here for instructions for use). Any patient who develops or has an increase in their oxygen requirement should be medically reviewed within 30 minutes.

The AIRVO 2 Humidifier flow rate should be set to meet or exceed the patients entire ventilatory demand, to ensure the desired FiO2 is actually inspired by the patient. High Flow Nasal Prong Therapy (HFNP), See the
min1 via facemask) or controlled oxygen with target saturation of 9498% prior to emergency percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Monitoring of SpO, Many children in the recovery phase of acute respiratory illnesses are characterised by ventilation/perfusion mismatch (e.g.

Assessment of Severe Respiratory Conditions guideline. Ensure straps and tubing are away from the patient's neck to prevent risk of airway obstruction. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine.

Where considering the application of oxygen therapy it is essential to perform a thorough clinical assessment of the child. The key principles will remain that oxygen is a treatment of hypoxemia and that oxygen should be prescribed to a target range. Martin, S., Martin, J., & Seigler, T. (2015). Available from: Effect of high flow oxygen on mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients in prehospital setting: randomised controlled trial, UK national COPD audit 2003: impact of hospital resources and organisation of care on patient outcome following admission for acute COPD exacerbation, Arterial blood gas reference values for sea level and an altitude of 1,400 meters, Diagnostic room-air pulse oximetry: effects of smoking, race, and sex, Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury, Consensus conference on mechanical ventilation January 2830, 1993 at Northbrook, Illinois, USA. (2013) High-Flow Nasal Prong Oxygen Therapy or Nasopharyngeal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Children With Moderate-to-Severe Respiratory Distress?www.pccmjounral.org September, Vol 14, No.3. Check on the individual flow meter for where to read the ball (i.e. Continuous pulse oximetry for 30 minutes post cessation of oxygen therapy
These masks are not commonly used but a non-rebreathing mask can provide higher concentration of FiO2 (> 60%) than is able to be provided with a standard face mask (which is approximately 40% - 50%)
We look forward to the publication of the results, which may provide some clarity for the optimal use of oxygen in acute myocardial infarction. Oxygen therapy: professional compliance with national guidelines. The recommended target saturation range for patients not at risk of T2RF is 9294%. The new children's guideline will provide comprehensive guidance on the emergency use of oxygen in paediatric healthcare and the adult guideline has been extended to include first responders and palliative care settings. This valve has been designed to minimize the risk of excessive pressure being delivered to the infant in the event that the nasal prongs seal around the infant's nares while the mouth is closed.

Change the adhesive tape weekly or more frequently as required, 4 LPM in infants/children under 2 years of age, Flow of 2 L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5 L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50 LPM), Flow of 2L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50LPM), Flow of 2L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50 LPM), Any patient who does not exhibit signs of clinical stabilization, as described below, within 2 hours of commencement of HFNP therapy should be reviewed by PICU outreach service. For nasal prong oxygen without humidification a maximum flow of: With the above flow rates humidification is not usually required. Note: In most low flow systems the flow is usually titrated (on the oxygen flow meter) and recorded in litres per minute (LPM). 4 503 504, Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Diagnosis, Management & Prevention of Bronchiolitis. The development of this nursing guideline was coordinated by John Kemp, Nurse Educator, Sugar Glider, and approved by the Nursing Clinical Effectiveness Committee. In life-threatening emergencies, oxygen can be given without a prescription until the patient is stable. Both hypoxaemia and hyperoxaemia are harmful. Oxygen therapy can be delivered using a low flow or high flow system. Tracheostomy HME - Heat Moisture Exchange (HME) with oxygen attachment
Please remember to read the
Commencement or Increase of Oxygen Therapy: 2. On device start up, a green traffic light confirms the AIRVO 2 is safe for use on a new patient. MR850 User Manual in conjunction with this Guideline
This system is simple and convenient to use. The AIRVO 2 Humidifier requires cleaning and disinfection between patients. THE FOLLOWING MAY BE UNDERTAKEN BY NURSES WITHOUT MEDICAL ORDERS: 1. Nasal prong flow rates of greater than 2 LPM (under 2 years of age) or 4 LPM (over 2 years of age), Nasal prong flow rates of greater than 1 LPM in neonates, Facial mask flow rates of greater than 5 LPM.


early warning scores) will also be included. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for infants with bronchiolitis: Pilot study.Journal of Paediatrics. OXY-VENT with Tubing: The adaptor sits over the TRACH-VENT and the tubing attaches to the oxygen source (flow meter).
Sitemap 8


 Journal of Pediatrics 156:634-38, Spentzas, T., Minarik, M., Patters, AB., Vinson, B. and Stidham, G. (2009) Children with respiratory distress treated with high-flow nasal cannula. (7th ed.).
Journal of Pediatrics 156:634-38, Spentzas, T., Minarik, M., Patters, AB., Vinson, B. and Stidham, G. (2009) Children with respiratory distress treated with high-flow nasal cannula. (7th ed.).  Oxygen is a drug and should be prescribed with a target saturation range. Check nares for patency - clear with suction as required.
Where oxygen weaning is successful, continuous pulse oximetry monitoring may be discontinued. Isolette use in paediatric wards, RCH internal link only. Due to this the following rules should be followed: Oxygen cylinders should be secured safely to avoid injury. It allows the oxygen therapy to continue during feeding/eating and the re-breathing of CO2 isn't a potential complication. Please consult user manuals for any other models in use. Frey, B., & Shann, F. (2003).
Oxygen is a drug and should be prescribed with a target saturation range. Check nares for patency - clear with suction as required.
Where oxygen weaning is successful, continuous pulse oximetry monitoring may be discontinued. Isolette use in paediatric wards, RCH internal link only. Due to this the following rules should be followed: Oxygen cylinders should be secured safely to avoid injury. It allows the oxygen therapy to continue during feeding/eating and the re-breathing of CO2 isn't a potential complication. Please consult user manuals for any other models in use. Frey, B., & Shann, F. (2003).  Additionally in some conditions (eg. Normal values and SpO 2 targets, Appendix A - Paediatric sizing guides for nasal prongs. The treatment of an acute or emergency situation where hypoxaemia or hypoxia is suspected, and if the child is in respiratory distress manifested by: use of accessory muscles: nasal flaring, intercostal or sternal recession, tracheal tug, Short term therapy e.g. To ensure the highest concentration of oxygen is delivered to the patient the reservoir bag needs to be inflated prior to placing on the patients face. Thank you for your interest in spreading the word on European Respiratory Society . HFNP nursing clinical guideline for more information. asthma, bronchiolitis, and pneumonia) and can be managed with SpO, Oxygen therapy should be closely monitored & assessed at regular intervals, Children with cyanotic congenital heart disease normally have SpO. 24(5): 323-8, Miyamoto, K. & Nishimura, M. Nasal Dryness Discomfit in Individuals Receiving Dry Oxygen via Nasal cannula Respiratory Care April (2008) Vol 35 No. Use of oxygen in continuous positive airway pressure ventilation systems, heliox and nitrous oxide mixtures, procedures that require conscious sedation, the peri-operative period and in track and trigger warning systems (e.g. O'Driscoll was paid an honorarium, by the ERS, for delivering a lecture on Emergency Oxygen Therapy at the ERS meeting in Vienna 2009.
Additionally in some conditions (eg. Normal values and SpO 2 targets, Appendix A - Paediatric sizing guides for nasal prongs. The treatment of an acute or emergency situation where hypoxaemia or hypoxia is suspected, and if the child is in respiratory distress manifested by: use of accessory muscles: nasal flaring, intercostal or sternal recession, tracheal tug, Short term therapy e.g. To ensure the highest concentration of oxygen is delivered to the patient the reservoir bag needs to be inflated prior to placing on the patients face. Thank you for your interest in spreading the word on European Respiratory Society . HFNP nursing clinical guideline for more information. asthma, bronchiolitis, and pneumonia) and can be managed with SpO, Oxygen therapy should be closely monitored & assessed at regular intervals, Children with cyanotic congenital heart disease normally have SpO. 24(5): 323-8, Miyamoto, K. & Nishimura, M. Nasal Dryness Discomfit in Individuals Receiving Dry Oxygen via Nasal cannula Respiratory Care April (2008) Vol 35 No. Use of oxygen in continuous positive airway pressure ventilation systems, heliox and nitrous oxide mixtures, procedures that require conscious sedation, the peri-operative period and in track and trigger warning systems (e.g. O'Driscoll was paid an honorarium, by the ERS, for delivering a lecture on Emergency Oxygen Therapy at the ERS meeting in Vienna 2009.  Why is a guideline for emergency oxygen necessary? This question is for testing whether or not you are a human visitor and to prevent automated spam submissions. A non-rebreathing face mask has an oxygen reservoir bag and one-way valve system which prevents exhaled gases mixing with fresh gas flow. As with the other delivery systems the inspired FiO2 depends on the flow rate of oxygen and varies according to the patient's minute ventilation.
Why is a guideline for emergency oxygen necessary? This question is for testing whether or not you are a human visitor and to prevent automated spam submissions. A non-rebreathing face mask has an oxygen reservoir bag and one-way valve system which prevents exhaled gases mixing with fresh gas flow. As with the other delivery systems the inspired FiO2 depends on the flow rate of oxygen and varies according to the patient's minute ventilation.  Oxygen therapy should be reduced or ceased if: This direction applies to patients treated with: See below nursing guidelines for additional guidance in assessment and monitoring: Unless clinically contraindicated, an attempt to wean oxygen therapy should be attempted at least once per shift. The FiO2 inspired will vary depending on the patient's inspiratory flow, mask fit/size and patient's respiratory rate. The
Oxygen is indicated in a patient who is suffering an acute MI who has saturation of 90%. Online ISSN: 2073-4735, Copyright 2022 by the European Respiratory Society. Only patients with COPD are at risk of T2RF. Emergency oxygen therapy: from guideline to implementation, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, University of Manchester, Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Salford Royal Foundation NHS Trust, Both authors contributed equally to this article, Audit of oxygen use in emergency ambulances and in a hospital emergency department, British Thoracic Society emergency oxygen audits, Short burst oxygen therapy in patients with COPD, BTS guideline for emergency oxygen use in adult patients, Effects of supplemental oxygen administration on coronary blood flow in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization, Systematic review of studies of the effect of hyperoxia on coronary blood flow, Postischemic reperfusion injury can be attenuated by oxygen tension control, Should stroke victims routinely receive supplemental oxygen? Patients who require an FiO2 greater than 50% require PICU medical review. Frequently Asked Questions. Position the tubing over the ears and secure behind the patients head.
Oxygen therapy should be reduced or ceased if: This direction applies to patients treated with: See below nursing guidelines for additional guidance in assessment and monitoring: Unless clinically contraindicated, an attempt to wean oxygen therapy should be attempted at least once per shift. The FiO2 inspired will vary depending on the patient's inspiratory flow, mask fit/size and patient's respiratory rate. The
Oxygen is indicated in a patient who is suffering an acute MI who has saturation of 90%. Online ISSN: 2073-4735, Copyright 2022 by the European Respiratory Society. Only patients with COPD are at risk of T2RF. Emergency oxygen therapy: from guideline to implementation, Manchester Academic Health Science Centre, University of Manchester, Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Salford Royal Foundation NHS Trust, Both authors contributed equally to this article, Audit of oxygen use in emergency ambulances and in a hospital emergency department, British Thoracic Society emergency oxygen audits, Short burst oxygen therapy in patients with COPD, BTS guideline for emergency oxygen use in adult patients, Effects of supplemental oxygen administration on coronary blood flow in patients undergoing cardiac catheterization, Systematic review of studies of the effect of hyperoxia on coronary blood flow, Postischemic reperfusion injury can be attenuated by oxygen tension control, Should stroke victims routinely receive supplemental oxygen? Patients who require an FiO2 greater than 50% require PICU medical review. Frequently Asked Questions. Position the tubing over the ears and secure behind the patients head.  Start 24 or 28% oxygen via a Venturi mask, then check blood gases. No difference was found between the two arms of the study in 30 day mortality or infarct size. Archives of Disease in Childhood. June, Vol.97, Issue 9, pg827-830, Ricard, J. Updated July 2017. Below is an image of the RT330 pressure relief valve. Simple nasal prongs are available in different sizes. Oxygen (via intact upper airway) via a simple face mask at flow rates of 4LPM does not routinely require humidification. Non-rebreathing face mask are not designed to allow added humidification. The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients not at risk of type II respiratory failure is 9498%.
Start 24 or 28% oxygen via a Venturi mask, then check blood gases. No difference was found between the two arms of the study in 30 day mortality or infarct size. Archives of Disease in Childhood. June, Vol.97, Issue 9, pg827-830, Ricard, J. Updated July 2017. Below is an image of the RT330 pressure relief valve. Simple nasal prongs are available in different sizes. Oxygen (via intact upper airway) via a simple face mask at flow rates of 4LPM does not routinely require humidification. Non-rebreathing face mask are not designed to allow added humidification. The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients not at risk of type II respiratory failure is 9498%. 
 Oxygen is a drug and should be prescribed. The humidifier should always be placed at a level below the patient's head. Nippers, I., & Sutton, A. Part I. European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, the ACCP and the SCCM, Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, The incidence and effect on outcome of hypoxemia in hospitalized medical patients, Reliability of pulse oximetry in titrating supplemental oxygen therapy in ventilator-dependent patients, Relationship between supranormal oxygen tension and outcome after resuscitation from cardiac arrest, The effect of supplemental oxygen on hypercapnia in subjects with obesity-associated hypoventilation: a randomized, crossover, clinical study, Randomised controlled trial of high concentration, Randomized controlled trial of high concentration oxygen in suspected community-acquired pneumonia, A randomized controlled trial of oxygen therapy in acute myocardial infarction Air Verses Oxygen In myocarDial infarction study (AVOID Study), A clinicians review of the respiratory microbiome, www.nrls.npsa.nhs.uk/resources/?entryid45=62811. ), Appendix A - Pediatric sizing guides for nasal prongs, Fisher and Paykel Optiflow junior range sizing guide. The child should appear clinically well. Respiratory Distress (work of breathing) should be mild, or there should be no work of breathing. The image below is of the RT330 circuit. 20 (6), 39-45. B.R.
Oxygen is a drug and should be prescribed. The humidifier should always be placed at a level below the patient's head. Nippers, I., & Sutton, A. Part I. European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, the ACCP and the SCCM, Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock, The incidence and effect on outcome of hypoxemia in hospitalized medical patients, Reliability of pulse oximetry in titrating supplemental oxygen therapy in ventilator-dependent patients, Relationship between supranormal oxygen tension and outcome after resuscitation from cardiac arrest, The effect of supplemental oxygen on hypercapnia in subjects with obesity-associated hypoventilation: a randomized, crossover, clinical study, Randomised controlled trial of high concentration, Randomized controlled trial of high concentration oxygen in suspected community-acquired pneumonia, A randomized controlled trial of oxygen therapy in acute myocardial infarction Air Verses Oxygen In myocarDial infarction study (AVOID Study), A clinicians review of the respiratory microbiome, www.nrls.npsa.nhs.uk/resources/?entryid45=62811. ), Appendix A - Pediatric sizing guides for nasal prongs, Fisher and Paykel Optiflow junior range sizing guide. The child should appear clinically well. Respiratory Distress (work of breathing) should be mild, or there should be no work of breathing. The image below is of the RT330 circuit. 20 (6), 39-45. B.R. 
 Bersten, A. D. & Soni, N. (2013). 91 - 95% for premature and term neonates (, 90% for infants with bronchiolitis (link to, The treatment of documented hypoxia/hypoxaemia as determined by SpO, Achieving targeted percentage of oxygen saturation (as per normal values unless a different target range is specified on the observation chart.).
Bersten, A. D. & Soni, N. (2013). 91 - 95% for premature and term neonates (, 90% for infants with bronchiolitis (link to, The treatment of documented hypoxia/hypoxaemia as determined by SpO, Achieving targeted percentage of oxygen saturation (as per normal values unless a different target range is specified on the observation chart.).  Oxygen is a treatment for hypoxaemia not breathlessness.
Oxygen is a treatment for hypoxaemia not breathlessness.  This system is useful in accurately delivering concentrations of oxygen (21 95%). Optiflow Nasal Prong junior and standard humidification and flow rate guide for Airvo. Humidification can be provided using either the MR850 Humidifier or the AIRVO 2 Humidifier. < 40 cm H20. Has two modes: Follow instructions in the
Level of consciousness (LOC) = alert, colour = pink, behaviour = normal. Sydney, Australia: Brink, F; T Duke, T., Evans, J. The minimum flow rate through any face mask or tracheostomy mask is 4 LPM as this prevents the possibility of CO2 accumulation and CO2 re-breathing. An orange traffic light confirms the AIRVO 2 has not been cleaned and disinfected since last use, and is not safe for use on a new patient. Humidification during oxygen therapy and non-invasive ventilation: do we need some and how much? Select a mask which best fits from the child's bridge of nose to the cleft of jaw, and adjust the nose clip and head strap to secure in place. Therefore, the results only apply to the short period of time between admission to hospital and primary PCI. Implementing the Rapid Response Report Oxygen Safety in Hospitals. Clinical assessment and documentation including but not limited to: cardiovascular, respiratory and neurological systems should be done at the commencement of each shift and with any change in patient condition. November, Vol.134, No.5, pge1474-e1502, Ramsey, K. (2012). The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients at risk of type II respiratory failure is 8892%. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier, Nagakumar, P. Doull, I. All high flow systems require humidification. Maintain efficient and economical use of oxygen. Non-Invasive Mode delivers gas at a comfortable level of humidity (31-36 degrees, >10mg/L). The Hudson Trach-Vent HME has a dead space of 10mL and is recommended for use in patients who have tidal volumes of 50mL and above. Oxygen delivery method selected depends on: Note: Oxygen therapy should not be delayed in the treatment of life threatening hypoxia. Where the Airvo2 is used as an oxygen delivery device the flow from this device is independent to the flow of oxygen. On arrival his oxygen saturation is 82% on room air, the correct course of action is: Do not give oxygen until blood gas results are available. Do nothing, he is known to have COPD and is often breathless and anxious. Trach-Vent's are changed daily or as required if contaminated or blocked by secretions. St. Clair, N., Touch, S. M., & Greenspan, S. (2001). For nasal prong oxygen withhumidification a maximum flow of: Optiflow nasal prongs are compatible for use in humidified low or high flow oxygen delivery. asthma, the hyperventilation of dry gases can compound bronchoconstriction. Clinical observations:
This system is useful in accurately delivering concentrations of oxygen (21 95%). Optiflow Nasal Prong junior and standard humidification and flow rate guide for Airvo. Humidification can be provided using either the MR850 Humidifier or the AIRVO 2 Humidifier. < 40 cm H20. Has two modes: Follow instructions in the
Level of consciousness (LOC) = alert, colour = pink, behaviour = normal. Sydney, Australia: Brink, F; T Duke, T., Evans, J. The minimum flow rate through any face mask or tracheostomy mask is 4 LPM as this prevents the possibility of CO2 accumulation and CO2 re-breathing. An orange traffic light confirms the AIRVO 2 has not been cleaned and disinfected since last use, and is not safe for use on a new patient. Humidification during oxygen therapy and non-invasive ventilation: do we need some and how much? Select a mask which best fits from the child's bridge of nose to the cleft of jaw, and adjust the nose clip and head strap to secure in place. Therefore, the results only apply to the short period of time between admission to hospital and primary PCI. Implementing the Rapid Response Report Oxygen Safety in Hospitals. Clinical assessment and documentation including but not limited to: cardiovascular, respiratory and neurological systems should be done at the commencement of each shift and with any change in patient condition. November, Vol.134, No.5, pge1474-e1502, Ramsey, K. (2012). The recommended oxygen target saturation range in patients at risk of type II respiratory failure is 8892%. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier, Nagakumar, P. Doull, I. All high flow systems require humidification. Maintain efficient and economical use of oxygen. Non-Invasive Mode delivers gas at a comfortable level of humidity (31-36 degrees, >10mg/L). The Hudson Trach-Vent HME has a dead space of 10mL and is recommended for use in patients who have tidal volumes of 50mL and above. Oxygen delivery method selected depends on: Note: Oxygen therapy should not be delayed in the treatment of life threatening hypoxia. Where the Airvo2 is used as an oxygen delivery device the flow from this device is independent to the flow of oxygen. On arrival his oxygen saturation is 82% on room air, the correct course of action is: Do not give oxygen until blood gas results are available. Do nothing, he is known to have COPD and is often breathless and anxious. Trach-Vent's are changed daily or as required if contaminated or blocked by secretions. St. Clair, N., Touch, S. M., & Greenspan, S. (2001). For nasal prong oxygen withhumidification a maximum flow of: Optiflow nasal prongs are compatible for use in humidified low or high flow oxygen delivery. asthma, the hyperventilation of dry gases can compound bronchoconstriction. Clinical observations:
 See guide below for recommended patient sizing and flow rates. < 90% for infants with bronchiolitis, The child with cyanotic heart disease reaches their baseline Sp0, Mechanical ventilation (do not alter other ventilator settings), Mask-BiPaP or CPAP (do not alter pressure or volume settings. Position the nasal prongs along the patients cheek and secure the nasal prongs on the patients face with adhesive tape. The next version of the BTS emergency oxygen guideline will be titled: BTS guideline for oxygen use in adults in healthcare and emergency settings and there will be a separate guideline on emergency use in children. Oxygen is not a flammable gas but it does support combustion (rapid burning). The pressure relief valve has been set to a limit of
Appendix A for further information regarding appropriate junior range sizing: Fisher and Paykel Optiflow junior range sizing guide, Fisher and Paykel Optiflow nasal cannula standard range, (
Schibler, A., Pham, T.,Dunster, K., Foster, K., Barlow, A., Gibbons, K., and Hough, J. (2014). If you require further information please click here for the
Medical gases, including air and oxygen, have a drying effect on mucous membranes resulting in airway damage. Therefore, humidification of nasal prong oxygen therapy is recommended. Enter multiple addresses on separate lines or separate them with commas. Intensive Care Med (2009) 35: 963-965. Check and document oxygen equipment set up at the commencement of each shift and with any change in patient condition.
See guide below for recommended patient sizing and flow rates. < 90% for infants with bronchiolitis, The child with cyanotic heart disease reaches their baseline Sp0, Mechanical ventilation (do not alter other ventilator settings), Mask-BiPaP or CPAP (do not alter pressure or volume settings. Position the nasal prongs along the patients cheek and secure the nasal prongs on the patients face with adhesive tape. The next version of the BTS emergency oxygen guideline will be titled: BTS guideline for oxygen use in adults in healthcare and emergency settings and there will be a separate guideline on emergency use in children. Oxygen is not a flammable gas but it does support combustion (rapid burning). The pressure relief valve has been set to a limit of
Appendix A for further information regarding appropriate junior range sizing: Fisher and Paykel Optiflow junior range sizing guide, Fisher and Paykel Optiflow nasal cannula standard range, (
Schibler, A., Pham, T.,Dunster, K., Foster, K., Barlow, A., Gibbons, K., and Hough, J. (2014). If you require further information please click here for the
Medical gases, including air and oxygen, have a drying effect on mucous membranes resulting in airway damage. Therefore, humidification of nasal prong oxygen therapy is recommended. Enter multiple addresses on separate lines or separate them with commas. Intensive Care Med (2009) 35: 963-965. Check and document oxygen equipment set up at the commencement of each shift and with any change in patient condition.  This study will enrol 490 patients and includes controlled oxygen therapy in the pre-hospital setting [34].
This study will enrol 490 patients and includes controlled oxygen therapy in the pre-hospital setting [34].  Evidence-Based Protocols to Guide Pulse Oximetry and Oxygen Weaning in Inpatient Children with Asthma and Bronchiolitis: A Pilot Project. Oxygen should be given to all patients having an acute stroke regardless of oxygen saturation. Follow the manufacturers Instructions for use for each device and setup.
Evidence-Based Protocols to Guide Pulse Oximetry and Oxygen Weaning in Inpatient Children with Asthma and Bronchiolitis: A Pilot Project. Oxygen should be given to all patients having an acute stroke regardless of oxygen saturation. Follow the manufacturers Instructions for use for each device and setup.  Secretions can become thick & difficult to clear or cause airway obstruction. (
Oxygen therapy and oxygen delivery principles (respiratory therapy). RCH predominantly uses the Fisher & Paykel MR850 Humidifier & AIRVO 2 Humidifier. The main safety feature of the RT330 Oxygen Therapy System is the pressure relief valve. Considerations when using a non-rebreathing face mask.
Secretions can become thick & difficult to clear or cause airway obstruction. (
Oxygen therapy and oxygen delivery principles (respiratory therapy). RCH predominantly uses the Fisher & Paykel MR850 Humidifier & AIRVO 2 Humidifier. The main safety feature of the RT330 Oxygen Therapy System is the pressure relief valve. Considerations when using a non-rebreathing face mask.  For most patients with COPD, target saturation range should be set at 8892% until blood gases are available. Neonatal Network. Supplemental oxygen relieves hypoxaemia but does not improve ventilation or treat the underlying cause of the hypoxaemia. The type of humidification device selected will depend on the oxygen delivery system in use, and the patient's requirements. Note: Some flow meters may deliver greater than the maximum flow indicated on the flow meter if the ball is set above the highest amount. A range of flow meters are available at RCH, 0-1 LPM, 0-2.5 LPM, 0-15 LPM. Publication is anticipated in 2014.
For most patients with COPD, target saturation range should be set at 8892% until blood gases are available. Neonatal Network. Supplemental oxygen relieves hypoxaemia but does not improve ventilation or treat the underlying cause of the hypoxaemia. The type of humidification device selected will depend on the oxygen delivery system in use, and the patient's requirements. Note: Some flow meters may deliver greater than the maximum flow indicated on the flow meter if the ball is set above the highest amount. A range of flow meters are available at RCH, 0-1 LPM, 0-2.5 LPM, 0-15 LPM. Publication is anticipated in 2014. 
 A patient with COPD and a history of hypercapnic respiratory failure becomes very breathless on the ward. Invasive Mode - delivers saturated gas as close to body temperature (37 degrees, 44mg/L) as possible. centre or top of ball), or dial (Perflow brand of flow meters) when setting the flow rate. In some conditions e.g. use of accessory muscles/nasal flaring - see Respiratory Distress on EMR), Ensure the individual MET criteria are observed regardless of oxygen requirements, Cease oxygen therapy entirely and maintain line of sight for approximately 5 minutes, LOC = alert, note lethargy or irritability, Non re-breather face mask (mask with oxygen reservoir bag and one-way valves which aims to prevent/reduce room air entrainment), Isolette - neonates (usually for use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit only), Face mask or tracheostomy mask used in conjunction with an, NB: There is separate CPG for HFNP use in the NICU (see, Cold, dry air increases heat and fluid loss.
A patient with COPD and a history of hypercapnic respiratory failure becomes very breathless on the ward. Invasive Mode - delivers saturated gas as close to body temperature (37 degrees, 44mg/L) as possible. centre or top of ball), or dial (Perflow brand of flow meters) when setting the flow rate. In some conditions e.g. use of accessory muscles/nasal flaring - see Respiratory Distress on EMR), Ensure the individual MET criteria are observed regardless of oxygen requirements, Cease oxygen therapy entirely and maintain line of sight for approximately 5 minutes, LOC = alert, note lethargy or irritability, Non re-breather face mask (mask with oxygen reservoir bag and one-way valves which aims to prevent/reduce room air entrainment), Isolette - neonates (usually for use in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit only), Face mask or tracheostomy mask used in conjunction with an, NB: There is separate CPG for HFNP use in the NICU (see, Cold, dry air increases heat and fluid loss.  Any patient who does not exhibit signs of clinical stabilization with 4 hours of commencement of HFNP should be considered for transfer to the PICU. Has two modes: Link to : Optiflow Nasal Prong Flow Rate Guide. NB: The above values are generalized to the paediatric population, for age/patient specific ranges please consult the covering medical team. Which of the following statements are true? Feeding adequate amounts orally. (See
For all critically ill patients, high concentration oxygen should be administered immediately until the patient is stable.
Any patient who does not exhibit signs of clinical stabilization with 4 hours of commencement of HFNP should be considered for transfer to the PICU. Has two modes: Link to : Optiflow Nasal Prong Flow Rate Guide. NB: The above values are generalized to the paediatric population, for age/patient specific ranges please consult the covering medical team. Which of the following statements are true? Feeding adequate amounts orally. (See
For all critically ill patients, high concentration oxygen should be administered immediately until the patient is stable.  Mosby's Skills.
Which of the following statements regarding oxygen prescribing are true? To ensure the patient is able to entrain room air around the nasal prongs and a complete seal is not created the prong size should be approximately half the diameter of the nares. Ralston, S.L., Lieberthal, A.S., Meissner, H.C., Alverston, B.K., Baley, J.E., Gadomski, A.M., Johnson, D.W., Light, M.J., Maraqa, n.F., Mendonca, E.A., Phelan, K.J., Zorc, J.J., Stanko-Lopp, D., Brown, M.A., Nathanson, I., Rosenblum, E., Sayles III, S. & Hernandez-Cancio, S. (2014) Pediatrics. Check nasal prong and tubing for patency, kinks or twists at any point in the tubing and clear or change prongs if necessary. (2014). However, if humidification is clinically indicated - set up as per the recommended guidelines for the specific equipment used. & Boyer, A. This study was flawed in that patients were randomised to treatment in hospital and most had received high-flow oxygen in the ambulance en route to hospital. Care and considerations of child with simple nasal prongs: If the required flow rate exceeds those as recommended above this may result in nasal discomfort and irritation of the mucous membranes. The aim of this guideline is to describe the indications and procedure for the use of oxygen therapy, and its modes of delivery. Oxygen administration in infants. May, Vol 50 (5) pp373-378, McKieman, C., Chua, L.C., Visintainer, P. and Allen, P. (2010) High Flow Nasal Cannulae Therapy in Infants with Bronchiolitis. The goal of oxygen delivery is to maintain targeted SpO2 levels in children through the provision of supplemental oxygen in a safe and effective way which is tolerated by infants and children to: Should an aerosol generating procedure be undertaken on a patient under droplet precautions then increase to airborne precautions by donning N95/P2 mask for at least the duration of the procedure. Follow the instructions in the disinfection kit manual: For routine cleaning instructions please refer to the following link:
The above values are expected target ranges. NOTE: We only request your email address so that the person you are recommending the page to knows that you wanted them to see it, and that it is not junk mail. (2012) Current Therapies for Bronchiolitis. We do not capture any email address. TRACH-VENT+: Alternatively a Hudson RCI HME - TRACH-VENT+ has an integrated oxygen side port which connects directly to oxygen tubing which is attached to the oxygen source (flow meter). Hourly checks should be made for the following: Hourly checks should be made and recorded on the patient observation chart for the following (unless otherwise directed by the treating medical team): respiratory distress (descriptive assessment - i.e. RT330 circuit - click here for instructions for use). Any patient who develops or has an increase in their oxygen requirement should be medically reviewed within 30 minutes.
Mosby's Skills.
Which of the following statements regarding oxygen prescribing are true? To ensure the patient is able to entrain room air around the nasal prongs and a complete seal is not created the prong size should be approximately half the diameter of the nares. Ralston, S.L., Lieberthal, A.S., Meissner, H.C., Alverston, B.K., Baley, J.E., Gadomski, A.M., Johnson, D.W., Light, M.J., Maraqa, n.F., Mendonca, E.A., Phelan, K.J., Zorc, J.J., Stanko-Lopp, D., Brown, M.A., Nathanson, I., Rosenblum, E., Sayles III, S. & Hernandez-Cancio, S. (2014) Pediatrics. Check nasal prong and tubing for patency, kinks or twists at any point in the tubing and clear or change prongs if necessary. (2014). However, if humidification is clinically indicated - set up as per the recommended guidelines for the specific equipment used. & Boyer, A. This study was flawed in that patients were randomised to treatment in hospital and most had received high-flow oxygen in the ambulance en route to hospital. Care and considerations of child with simple nasal prongs: If the required flow rate exceeds those as recommended above this may result in nasal discomfort and irritation of the mucous membranes. The aim of this guideline is to describe the indications and procedure for the use of oxygen therapy, and its modes of delivery. Oxygen administration in infants. May, Vol 50 (5) pp373-378, McKieman, C., Chua, L.C., Visintainer, P. and Allen, P. (2010) High Flow Nasal Cannulae Therapy in Infants with Bronchiolitis. The goal of oxygen delivery is to maintain targeted SpO2 levels in children through the provision of supplemental oxygen in a safe and effective way which is tolerated by infants and children to: Should an aerosol generating procedure be undertaken on a patient under droplet precautions then increase to airborne precautions by donning N95/P2 mask for at least the duration of the procedure. Follow the instructions in the disinfection kit manual: For routine cleaning instructions please refer to the following link:
The above values are expected target ranges. NOTE: We only request your email address so that the person you are recommending the page to knows that you wanted them to see it, and that it is not junk mail. (2012) Current Therapies for Bronchiolitis. We do not capture any email address. TRACH-VENT+: Alternatively a Hudson RCI HME - TRACH-VENT+ has an integrated oxygen side port which connects directly to oxygen tubing which is attached to the oxygen source (flow meter). Hourly checks should be made for the following: Hourly checks should be made and recorded on the patient observation chart for the following (unless otherwise directed by the treating medical team): respiratory distress (descriptive assessment - i.e. RT330 circuit - click here for instructions for use). Any patient who develops or has an increase in their oxygen requirement should be medically reviewed within 30 minutes.  The AIRVO 2 Humidifier flow rate should be set to meet or exceed the patients entire ventilatory demand, to ensure the desired FiO2 is actually inspired by the patient. High Flow Nasal Prong Therapy (HFNP), See the
min1 via facemask) or controlled oxygen with target saturation of 9498% prior to emergency percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Monitoring of SpO, Many children in the recovery phase of acute respiratory illnesses are characterised by ventilation/perfusion mismatch (e.g.
The AIRVO 2 Humidifier flow rate should be set to meet or exceed the patients entire ventilatory demand, to ensure the desired FiO2 is actually inspired by the patient. High Flow Nasal Prong Therapy (HFNP), See the
min1 via facemask) or controlled oxygen with target saturation of 9498% prior to emergency percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Monitoring of SpO, Many children in the recovery phase of acute respiratory illnesses are characterised by ventilation/perfusion mismatch (e.g.  Assessment of Severe Respiratory Conditions guideline. Ensure straps and tubing are away from the patient's neck to prevent risk of airway obstruction. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine.
Assessment of Severe Respiratory Conditions guideline. Ensure straps and tubing are away from the patient's neck to prevent risk of airway obstruction. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine.  Where considering the application of oxygen therapy it is essential to perform a thorough clinical assessment of the child. The key principles will remain that oxygen is a treatment of hypoxemia and that oxygen should be prescribed to a target range. Martin, S., Martin, J., & Seigler, T. (2015). Available from: Effect of high flow oxygen on mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients in prehospital setting: randomised controlled trial, UK national COPD audit 2003: impact of hospital resources and organisation of care on patient outcome following admission for acute COPD exacerbation, Arterial blood gas reference values for sea level and an altitude of 1,400 meters, Diagnostic room-air pulse oximetry: effects of smoking, race, and sex, Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury, Consensus conference on mechanical ventilation January 2830, 1993 at Northbrook, Illinois, USA. (2013) High-Flow Nasal Prong Oxygen Therapy or Nasopharyngeal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Children With Moderate-to-Severe Respiratory Distress?www.pccmjounral.org September, Vol 14, No.3. Check on the individual flow meter for where to read the ball (i.e. Continuous pulse oximetry for 30 minutes post cessation of oxygen therapy
These masks are not commonly used but a non-rebreathing mask can provide higher concentration of FiO2 (> 60%) than is able to be provided with a standard face mask (which is approximately 40% - 50%)
We look forward to the publication of the results, which may provide some clarity for the optimal use of oxygen in acute myocardial infarction. Oxygen therapy: professional compliance with national guidelines. The recommended target saturation range for patients not at risk of T2RF is 9294%. The new children's guideline will provide comprehensive guidance on the emergency use of oxygen in paediatric healthcare and the adult guideline has been extended to include first responders and palliative care settings. This valve has been designed to minimize the risk of excessive pressure being delivered to the infant in the event that the nasal prongs seal around the infant's nares while the mouth is closed.
Where considering the application of oxygen therapy it is essential to perform a thorough clinical assessment of the child. The key principles will remain that oxygen is a treatment of hypoxemia and that oxygen should be prescribed to a target range. Martin, S., Martin, J., & Seigler, T. (2015). Available from: Effect of high flow oxygen on mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients in prehospital setting: randomised controlled trial, UK national COPD audit 2003: impact of hospital resources and organisation of care on patient outcome following admission for acute COPD exacerbation, Arterial blood gas reference values for sea level and an altitude of 1,400 meters, Diagnostic room-air pulse oximetry: effects of smoking, race, and sex, Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury, Consensus conference on mechanical ventilation January 2830, 1993 at Northbrook, Illinois, USA. (2013) High-Flow Nasal Prong Oxygen Therapy or Nasopharyngeal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure for Children With Moderate-to-Severe Respiratory Distress?www.pccmjounral.org September, Vol 14, No.3. Check on the individual flow meter for where to read the ball (i.e. Continuous pulse oximetry for 30 minutes post cessation of oxygen therapy
These masks are not commonly used but a non-rebreathing mask can provide higher concentration of FiO2 (> 60%) than is able to be provided with a standard face mask (which is approximately 40% - 50%)
We look forward to the publication of the results, which may provide some clarity for the optimal use of oxygen in acute myocardial infarction. Oxygen therapy: professional compliance with national guidelines. The recommended target saturation range for patients not at risk of T2RF is 9294%. The new children's guideline will provide comprehensive guidance on the emergency use of oxygen in paediatric healthcare and the adult guideline has been extended to include first responders and palliative care settings. This valve has been designed to minimize the risk of excessive pressure being delivered to the infant in the event that the nasal prongs seal around the infant's nares while the mouth is closed.  Change the adhesive tape weekly or more frequently as required, 4 LPM in infants/children under 2 years of age, Flow of 2 L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5 L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50 LPM), Flow of 2L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50LPM), Flow of 2L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50 LPM), Any patient who does not exhibit signs of clinical stabilization, as described below, within 2 hours of commencement of HFNP therapy should be reviewed by PICU outreach service. For nasal prong oxygen without humidification a maximum flow of: With the above flow rates humidification is not usually required. Note: In most low flow systems the flow is usually titrated (on the oxygen flow meter) and recorded in litres per minute (LPM). 4 503 504, Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Diagnosis, Management & Prevention of Bronchiolitis. The development of this nursing guideline was coordinated by John Kemp, Nurse Educator, Sugar Glider, and approved by the Nursing Clinical Effectiveness Committee. In life-threatening emergencies, oxygen can be given without a prescription until the patient is stable. Both hypoxaemia and hyperoxaemia are harmful. Oxygen therapy can be delivered using a low flow or high flow system. Tracheostomy HME - Heat Moisture Exchange (HME) with oxygen attachment
Please remember to read the
Commencement or Increase of Oxygen Therapy: 2. On device start up, a green traffic light confirms the AIRVO 2 is safe for use on a new patient. MR850 User Manual in conjunction with this Guideline
This system is simple and convenient to use. The AIRVO 2 Humidifier requires cleaning and disinfection between patients. THE FOLLOWING MAY BE UNDERTAKEN BY NURSES WITHOUT MEDICAL ORDERS: 1. Nasal prong flow rates of greater than 2 LPM (under 2 years of age) or 4 LPM (over 2 years of age), Nasal prong flow rates of greater than 1 LPM in neonates, Facial mask flow rates of greater than 5 LPM.
Change the adhesive tape weekly or more frequently as required, 4 LPM in infants/children under 2 years of age, Flow of 2 L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5 L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50 LPM), Flow of 2L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50LPM), Flow of 2L/kg/min up to 12kg, plus 0.5L/kg/min for each kg above 12kg (to a maximum of 50 LPM), Any patient who does not exhibit signs of clinical stabilization, as described below, within 2 hours of commencement of HFNP therapy should be reviewed by PICU outreach service. For nasal prong oxygen without humidification a maximum flow of: With the above flow rates humidification is not usually required. Note: In most low flow systems the flow is usually titrated (on the oxygen flow meter) and recorded in litres per minute (LPM). 4 503 504, Clinical Practice Guidelines: The Diagnosis, Management & Prevention of Bronchiolitis. The development of this nursing guideline was coordinated by John Kemp, Nurse Educator, Sugar Glider, and approved by the Nursing Clinical Effectiveness Committee. In life-threatening emergencies, oxygen can be given without a prescription until the patient is stable. Both hypoxaemia and hyperoxaemia are harmful. Oxygen therapy can be delivered using a low flow or high flow system. Tracheostomy HME - Heat Moisture Exchange (HME) with oxygen attachment
Please remember to read the
Commencement or Increase of Oxygen Therapy: 2. On device start up, a green traffic light confirms the AIRVO 2 is safe for use on a new patient. MR850 User Manual in conjunction with this Guideline
This system is simple and convenient to use. The AIRVO 2 Humidifier requires cleaning and disinfection between patients. THE FOLLOWING MAY BE UNDERTAKEN BY NURSES WITHOUT MEDICAL ORDERS: 1. Nasal prong flow rates of greater than 2 LPM (under 2 years of age) or 4 LPM (over 2 years of age), Nasal prong flow rates of greater than 1 LPM in neonates, Facial mask flow rates of greater than 5 LPM. 
 early warning scores) will also be included. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for infants with bronchiolitis: Pilot study.Journal of Paediatrics. OXY-VENT with Tubing: The adaptor sits over the TRACH-VENT and the tubing attaches to the oxygen source (flow meter).
early warning scores) will also be included. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for infants with bronchiolitis: Pilot study.Journal of Paediatrics. OXY-VENT with Tubing: The adaptor sits over the TRACH-VENT and the tubing attaches to the oxygen source (flow meter).