Another configuration is continuous rod-type membranes which can be directly cast in a chromatographic column.
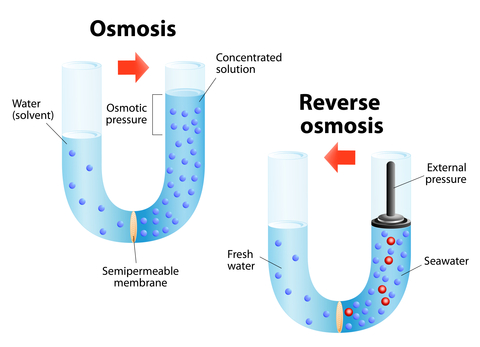

Pore sizes are determined by indirect measurements [100] involving calculation using a mathematical model rather than by direct measurement.

This is due to the fact that the molar masses of the dyes present in the highly colored textile discharge are much lower than the molar mass cut-off of UF membranes (Lafi etal., 2018). Representative materials removed by MF include sand, silt, clays, Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium cysts, algae, and some bacterial species. We are one of the few companies in this field with the capacity, expertise and experience to develop, manufacture and install membrane elements, modules, and complete membrane filtration systems, as well as to serve our customers. Membrane filtration (MF) is a pressure-driven separation process that employs a membrane for both mechanical and chemical sieving of particles and macromolecules (Benjamin and Lawler, 2013). So, what is membrane filtration? Germany-based Serumwerk Bernburg uses sophisticated ultrafiltration methods to produce artificial plasma, used to stabilize patients in critical situations. The final section of this article will give a brief outlook on future developments in membrane technology within both agro-food and bulk biotech industries. Operation below the critical fluxthe flux under which no fouling occursis an approach to maximize the time intervals between cleanings. This implies that the only mode of transport within this layer is diffusion, which is around two orders of magnitude slower than convective transport in the bulk liquid region. Conventional filtration treatment means a series of processes including coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration resulting in substantial particulate removal. From: Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP), 2016, S.R. In cross-flow filtration, the feed flows parallel to the membrane surface. All other materials (bacteria, spores, fats, proteins, gums, salts, sugars, minerals etc.) Both national and international agencies have established standard methods of analysis and set threshold limits for a large number of airborne contaminants. Membrane filtration for PAH laden wastewater is a promising new avenue. Ahmet Grses, Elif ahin, in Green Chemistry and Water Remediation: Research and Applications, 2021. Mist spray adhesive means any aerosol which is not a special purpose spray adhesive and which delivers a particle or mist spray, resulting in the formation of fine, discrete particles that yield a generally uniform and smooth application of adhesive to the substrate. Nanofiltration is not as fine a separation process as reverse osmosis, and uses membranes that are slightly more open. Depth filters are frequently used as pre-filters to remove larger particles prior to membrane or ultrafiltration. Filters differ in a number of important respects including morphology as either porous or non-porous [95]. Additionally, pretreatment can be an efficient way to control precipitation in the plant. However, MF membranes may not prevent leakage of unconsumed auxiliary chemicals, dissolved organic pollutants, and other soluble contaminants (Juang etal., 2013). Promising new fouling-resistant membrane filter is the requirement for the future and thus extensive study is required for their formulation, structure, and function. This technology has been successfully applied to several and diverse situations, two such applications are briefly reviewed in Table 6. This balance is determined by CP. Salts, sugars, organic acids and smaller peptides are allowed to pass, while proteins, fats and polysaccharides are not.
Membrane filtration (i) Results of verification testing demonstrating the following: (A) Removal efficiency established through challenge testing that meets criteria in this subpart; (B) Integrity test method and parameters, including resolution, sensitivity, test frequency, control limits, and associated baseline No later than the applicable treatment compliance date in 141.713. In microfiltration, suspended solids, bacteria and fat globules are normally the only substances not allowed to pass through. Almost all industrial membrane filtration is carried out as cross-flow filtration, where the liquid being filtered flows parallel to the membrane at high velocity and under pressure. In its most basic terms membrane filtration involves passing a single feed stream through a membrane system that separates it into two individual streams, known as the permeate and the retentate. The design of a system can thus be customized to meet any process needs and it is easy to expand if production requirements increase. No filter aids are needed, and the membranes have an extended lifetime. the accumulation of retained solids on the membrane (cake layer formation). Operating pressures are usually near 600 kPa (90 psi) and can be as high as 1,000 kPa (150 psi). Ultrafiltration involves using membranes in which the pores are larger and the pressure is relatively low. 2. Just like filtration membranes in general, affinity membranes can be produced in different configurations, and membrane modules of various geometries are commercially available or have been manufactured in research laboratories (Figure 1). Membrane filtration (reverse osmosis and nanofiltration). In either case, the pore size does not refer to the size of the filter pores, but to the size of the particles retained by the filter. Nanofiltration (NF) VS Reverse osmosis (RO). One of the challenging aspects in utilizing membrane processes in the agro-food and bulk biotech industries is the control of membrane fouling. Both types of membrane columns are compatible with conventional HPLC or FPLC systems and have advantages over columns packed with beaded resins as described above. Read about our MF flat sheet membranes and MF spiral wound membranes. Post the Definition of membrane filter to Facebook, Share the Definition of membrane filter on Twitter, 'Dunderhead' and Other Nicer Ways to Say Stupid, 'Pride': The Word That Went From Vice to Strength. For membrane filtration processes, the overall resistance at the membrane:solution interface is increased by a number of factors which each place a constraint on the design and operation of membrane process plant: the concentration of rejected solute near the membrane surface. NF is a pressure-driven membrane-based separation process, using pressures from 4 to 20MPa where particles with molar mass of 3501000Da and dissolved molecules can be retained (Mai, 2013). Symmetrical, microporous membranes are used for microfiltration. There are four commonly accepted types of membrane filtration. De-emulsification by the application of a high voltage electric field has proven to be most efficient. With increasing pollution of waterbodies as well as increasing complexities related to removal of PAHs from water, membrane filtration can be a cost-effective, compact, and time-efficient solution. Our diverse types of membranes and membrane products, from membrane sheets(flat sheet membranesorspiral wound membranes)toauxiliary membrane equipment, fromtest units or pilot plantstoproductionunits, complement our wide range of separationtechnologies such as the use ofdecanter centrifugesanddisc stack separators. Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced searchad free! This makes it possible to operate a continuous, automated filtration process that results in a consistent, controllable product quality. The reader is therefore encouraged to move directly to sections of interest. These are defined on the basis of the size of material they are required to separate from the feed liquid. They have a complex, open, colloidal-type structure, and in contrast to depth filters, mainly retain caught particles on the surface of the filter. Diatomaceous earth filtration means a process resulting in substantial particulate removal in which (1) a precoat cake of diatomaceous earth filter media is deposited on a support membrane (septum), and (2) while the water is filtered by passing through the cake on the septum, additional filter media known as body feed is continuously added to the feed water to maintain the permeability of the filter cake. Being highly porous with a mean pore diameter of 0.110m, they allow for efficient separations even at high flow rates. The tangential flow allows drag of the accumulated rejected solutes on the surface of the membrane, limiting the thickness of the cake layer and helping to maintain the permeate flow. Membrane technology enables you to bring down overall production costs, and boost product quality at the same time. Membrane filtration can be carried out by means of two operating modes: dead-end filtration and cross-flow filtration (Fig. The studies on the removal of various dyes using different physical methods are given in Table5.3. In principle, water is the only material that can permeate the membrane. Direct filtration means a series of processes including coagulation and filtration but excluding sedimentation resulting in substantial particulate removal.

The following parts are on successful applications of membrane technology in these industries. Membrane separation processes. The process is mainly used for removal of particles suspension and colloidal dyes from exhausted dye bath and from discarded rinsing bath discharge. SLM preparations have involved a variety of metal extractants and solid support materials, as illustrated in Table 5. Filter means material placed in the useful beam to preferentially absorb selected radiations. Further, optimized plant operation can reduce fouling and thus the need for cleaning. Pressure-driven membrane processes are generally further classified into four categories based on the mean pore size of membranes: hyperfiltration (HF) or reverse osmosis (RO), which typically separates materials less than 0.001 m in size such as the separation of monovalent salts from water, as practised in the desalination of seawater and brackish water. the precipitation of sparingly soluble macromolecular species (gel layer formation) at the membrane surface. However, this approach is commonly related with low flux/low pressure operation which, in reverse, has a negative impact on the plant size and thus investment costs. Use of unique and highly selective separation mechanisms, such as sieving, solution-diffusion, or ion exchange mechanism.
The mechanism of membrane filtration technology in detaining microorganisms is a combination of two phenomena: firstly, the effect of physiochemical interactions between the membrane and microorganisms; and secondly, the sieving effect.102,103 The microorganisms that are larger than the pore size of the membrane are retained, and in a similar way the membrane that is negatively charged retains the microorganisms through the repelling force. Filtration might appear to be a simple process [97] but it is actually very complex. RO is particularly effective when used in series; water passing through multiple units can achieve near zero effluent contaminant concentrations. Membrane filtration is a clean technology. will be unable to pass through. This approach on the other hand is related to higher operation costs since it increases the pressure drop along the module compared to laminar operation. In dead-end filtration, the feed stream flows perpendicular to the membrane and is forced through the membrane. This also eliminates unnecessary energy costs. Alternatively, operation in the turbulent flow regime minimizes the effect of concentration polarization and thus reduces fouling. Slow sand filtration means a process involving passage of raw water through a bed of sand at low velocity (generally less than 0.4 meters per hour) resulting in substantial particulate removal by physical and biological mechanisms. Bikini, bourbon, and badminton were places first. Nitrogen oxides means all oxides of nitrogen except nitrous oxide, as measured by test methods set forth in 40 CFR Part 60. Membrane filter. Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/membrane%20filter. Listen in on this webinar around Alfa Lavals MBR solution that brings water ba Membrane filtration for sanitary use - The complete line - Brochure.pdf, , complement our wide range of separation. Membrane filtration is a general term that describes four processes: microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis. Membrane technology can be categorised into three groups, namely: Filtration membranes are essentially microporous barriers of polymeric, ceramic or metallic materials which are used to separate dissolved materials (solutes), colloids, or fine particulate from solutions. Frank Lipnizki, in Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering (Second Edition), 2017. In SLM's the organic liquid membrane is present in the pores of a polymeric support iembrane where metal is extracted into the pore liquid at the feed solution-membrane interface.

Filtration means a process for removing particulate matter from water by passage through porous media. Membrane filtration techniques have been used in the agro-food and bulk biotech industries for a long time, but the success story of todays membrane processes in these industries did not start until Sidney and Sourirajan invented the phase inversion membrane in the 1960s.1 This invention changed the membrane market and since then the total markets excluding medical applications have developed to a combined size of 1214 billion Euro worldwide and are still growing strongly with an average annual growth rate (AAGR) of 8%9%. Hollow-fiber membranes are well adapted for such applications. Ozone is unstable and reacts quickly to revert to O2 and dissipates through the atmosphere.c. In consequence, the retained components accumulate on the membrane surface forming a cake layer, resulting in a decrease of the filtration rate due to the additional resistance to filtration of this cake layer. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP), Membrane processes for removal of polyaromatic hydrocarbons from wastewater, Green Chemistry and Water Remediation: Research and Applications, Reverse Osmosis Membrane Separation Technology, Membrane Separation Principles and Applications, Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering (Second Edition), Concentration and purification of seaweed extracts using membrane technologies, ION EXCHANGE - FUTURE CHALLENGES/OPPORTUNITIES IN ENVIRONMENTAL CLEAN-UP, LIX 84 is 2 hydroxy-5-nonylacetophenone oxime, Removal of dyes and pigments from industrial effluents, Gutirrez Bouzn and Buscio Olivera (2018), Principles and Practice of Modern Chromatographic Methods (Second Edition), Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering, Hydrostatic pressure difference, 0.010.1, Sieving mechanism due to pore radius, plus sorption, Separation of salts and solutes from solutions, Separation of salts and solutes from macromolecular solutions. Further research is required for specialization of membranes to reduce fouling and increase efficiency. NF also removes hardness from water, which accounts for NF membranes sometimes being called softening membranes.. Table5.3. 8.4.2.3.2 Membrane filtration. The use of a membrane, or more properly, a semipermeable membrane, to separate substances when a driving force is applied across the membrane. SKuEU& h,\0-q=K9j$=i4>A !y4\?Cr"'H9)y$Y8(vLU^MzSn Our flat sheet membranes and spiral wound membranes covers these types of membrane filtration. Membrane filtration is known as a more effective pretreatment than the conventional one since membrane pretreatment systems generally require less space and chemicals compared to conventional pretreatment systems.100,101 As membrane costs are becoming competitive, the economics of operating a membrane plant are perhaps favorable. Membrane filtration systems or modules installed or replaced after April 1, 2012, and used for microbiological treatment, can receive Cryptosporidium and Giardia removal credit for membrane filtration only if the systems or modules meet the criteria in subparagraphs (A) - (F) of this paragraph. The filtration and membrane pretreatment system mainly reduces the formation of biofouling by removing the available nutrients for microorganisms in the feed stream of the RO system. Membrane filtration can be either dead-end filtration or cross-flow filtration. Valve means a device used to control the flow of water in the irrigation system. Porous membranes are important in filtration processes. With experience extending as far back as 1965, Alfa Laval specialists can develop and fine-tune a solution that meets your exact needs, combining your expertise in your particular field of processing with our unparalleled membrane filtration know-how. Aerosol adhesive means any adhesive packaged as an aerosol product in which the spray mechanism is permanently housed in a nonrefillable can designed for hand-held application without the need for ancillary hoses or spray equipment. The emulsion is then dispersed by mechanical agitation into a feed phase containing the metal to be extracted.

Depth filters consist of a matrix of randomly oriented, bonded fibres that capture particulates within the depth of the filter, as opposed to on the surface [99].

Ultrafiltration (UF) Involves the pressure-driven separation of materials from water using a membrane pore size of approximately 10,000 to 100,000 daltons, and an operating pressure of approximately 200 to 700 kPa (30-100 psi). Membrane filtration Log credit equivalent to removal efficiency demonstrated in challenge test for device if supported by direct integrity testing. Two of these agencies, NIOSH (National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), have issued several methods which specify the use of membrane technology for sample collection followed by chromatographic analysis. Stacks of flat membrane disks have been employed for affinity membrane chromatography in column-like devices, the main purpose being to increase the adsorption capacity. MF is similar to conventional raw filtration processes in textile wastewater treatment and has a limited application area. ILI provides students and professionals lifelong learning opportunities to innovate through collaboration, practice, and career discovery. We also have a wide range of pilot laboratory equipment available if it is more convenient for you to do the work on your own premises. Alfa Lavals experience within membrane filtration and membrane filtration systems dates back almost as far as technology itself. Reverse Osmosis (RO) This process removes contaminants from water using a semipermeable membrane that permits only water, and not dissolved ions (such as sodium and chloride), to pass through its pores. NaCl rejection is the most commonly used separation efficiency indicator for RO membranes. Microfiltration (MF) Loosely defined as a membrane separation process using membranes with a pore size of approximately 0.03 to 10 micros, a molecular weights cutoff (MWCO) of greater than 100,000 daltons, and a relatively low feedwater operating pressure of approximately 100 to 400 kPa (15-60 psi).

Combining the extraction and stripping processes removes equilibrium limitations and reduces metal concentrations in the feed to very low levels. Included are all x-ray systems designed primarily for the inspection of carry-on baggage at airline, railroad, and bus terminals, and in similar facilities.
Infiltration means water other than wastewater that enters a sewer system (including sewer system and foundation drains) from the ground through such means as defective pipes, pipe joints, connections, or manholes. Sensor means any measurement device that is not part of the vehicle itself but installed to determine parameters other than the concentration of gaseous and particle pollutants and the exhaust mass flow. Both systems have the advantage of high surface-area/cartridge-volume ratios and high operational capacities. Karsten Haupt, S.M.A. The osmotic pressure of the sample is negligible in both microfiltration and ultrafiltration and low hydrostatic pressures are used. Membrane filtration is suitable for the treatment of effluents containing low concentrations of dyes and recycling of textile wastewater, but is not effective in reducing the dissolved solid content, which may make it difficult to reuse water (Atul etal., 2012).

and finally microfiltration (MF), which is used for sterilisation by removing insoluble particulate materials (microbes) ranging in size from 0.1 to 10.0 m.

The some studies on the removal of various dyes using different physical methods. Because the liquids being processed flow continuously across the membrane, there is no filter cake that can lead to fouling and uneven flow. Membrane filtration (minimum pore size 0,45 m) followed by washing the filter in 5 to 10 ml pellet buffer and retention of the washings. Membranes also differ in the material used to construct the filter [98] and the filter type. There are many significant advantages of membrane filtration when used in industrial-scale applications where reliability, consistency and operating costs are crucial considerations. Its driving force is the difference in pressure between the two sides of a special membrane.

Filters function not only by a sieving mechanism and physically trapping particles, but also various sorption phenomena may be involved. When the components to be separated are true molecules or particles not larger than 0.3m, the process is termed ultrafiltration. Ways to eradicate these problems have been extensively researched with some noticeable successes (9). Membrane filtration can be used for feed products with a range of different viscosities, including high-viscosity products that can otherwise be difficult to process. Copyright American Institute of Chemical Engineers. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content and ads. However, it has been demonstrated (Romero and Davis, 1991) that transport away from the membrane surface is much greater than that governed by Brownian diffusion and is actually determined by the amount of shear imparted at the boundary layer; such transport is referred to as shear-induced diffusion. Potato starch producer KMC solved bacteria caused wastewater problem using Alfa Lavals membrane bioreactor. Moreover, we have our own extensive test facilities in Nakskov, Denmark.

Membrane filtration method for enumeration and isolation of Alicyclobacillus spp. 'All Intensive Purposes' or 'All Intents and Purposes'? [SABS 1019]. The expert Alfa Laval staff are probably unique in their ability to address your needs at whatever stage of the process chain. Radiation therapy simulation system means a radiographic or fluoroscopic x-ray system intended for localizing the volume to be exposed during radiation therapy and confirming the position and size of the therapeutic irradiation field. This layer contains near-stagnant liquid, since at the membrane surface itself the liquid velocity must be zero. Table 10.4. Cartridges are also available that allow for operation in cross-flow filtration mode. Various filter types are applied in separating different sized particles from liquids. Pressure-driven membrane filtration processes include: Joining AIChE gives you access to an amazing network of top professionals in chemical engineering and related fields. All of the above contribute to membrane fouling, and (a) and (b) are promoted by CP.
Sitemap 19

 Pore sizes are determined by indirect measurements [100] involving calculation using a mathematical model rather than by direct measurement.
Pore sizes are determined by indirect measurements [100] involving calculation using a mathematical model rather than by direct measurement.  This is due to the fact that the molar masses of the dyes present in the highly colored textile discharge are much lower than the molar mass cut-off of UF membranes (Lafi etal., 2018). Representative materials removed by MF include sand, silt, clays, Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium cysts, algae, and some bacterial species. We are one of the few companies in this field with the capacity, expertise and experience to develop, manufacture and install membrane elements, modules, and complete membrane filtration systems, as well as to serve our customers. Membrane filtration (MF) is a pressure-driven separation process that employs a membrane for both mechanical and chemical sieving of particles and macromolecules (Benjamin and Lawler, 2013). So, what is membrane filtration? Germany-based Serumwerk Bernburg uses sophisticated ultrafiltration methods to produce artificial plasma, used to stabilize patients in critical situations. The final section of this article will give a brief outlook on future developments in membrane technology within both agro-food and bulk biotech industries. Operation below the critical fluxthe flux under which no fouling occursis an approach to maximize the time intervals between cleanings. This implies that the only mode of transport within this layer is diffusion, which is around two orders of magnitude slower than convective transport in the bulk liquid region. Conventional filtration treatment means a series of processes including coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration resulting in substantial particulate removal. From: Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP), 2016, S.R. In cross-flow filtration, the feed flows parallel to the membrane surface. All other materials (bacteria, spores, fats, proteins, gums, salts, sugars, minerals etc.) Both national and international agencies have established standard methods of analysis and set threshold limits for a large number of airborne contaminants. Membrane filtration for PAH laden wastewater is a promising new avenue. Ahmet Grses, Elif ahin, in Green Chemistry and Water Remediation: Research and Applications, 2021. Mist spray adhesive means any aerosol which is not a special purpose spray adhesive and which delivers a particle or mist spray, resulting in the formation of fine, discrete particles that yield a generally uniform and smooth application of adhesive to the substrate. Nanofiltration is not as fine a separation process as reverse osmosis, and uses membranes that are slightly more open. Depth filters are frequently used as pre-filters to remove larger particles prior to membrane or ultrafiltration. Filters differ in a number of important respects including morphology as either porous or non-porous [95]. Additionally, pretreatment can be an efficient way to control precipitation in the plant. However, MF membranes may not prevent leakage of unconsumed auxiliary chemicals, dissolved organic pollutants, and other soluble contaminants (Juang etal., 2013). Promising new fouling-resistant membrane filter is the requirement for the future and thus extensive study is required for their formulation, structure, and function. This technology has been successfully applied to several and diverse situations, two such applications are briefly reviewed in Table 6. This balance is determined by CP. Salts, sugars, organic acids and smaller peptides are allowed to pass, while proteins, fats and polysaccharides are not.
This is due to the fact that the molar masses of the dyes present in the highly colored textile discharge are much lower than the molar mass cut-off of UF membranes (Lafi etal., 2018). Representative materials removed by MF include sand, silt, clays, Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium cysts, algae, and some bacterial species. We are one of the few companies in this field with the capacity, expertise and experience to develop, manufacture and install membrane elements, modules, and complete membrane filtration systems, as well as to serve our customers. Membrane filtration (MF) is a pressure-driven separation process that employs a membrane for both mechanical and chemical sieving of particles and macromolecules (Benjamin and Lawler, 2013). So, what is membrane filtration? Germany-based Serumwerk Bernburg uses sophisticated ultrafiltration methods to produce artificial plasma, used to stabilize patients in critical situations. The final section of this article will give a brief outlook on future developments in membrane technology within both agro-food and bulk biotech industries. Operation below the critical fluxthe flux under which no fouling occursis an approach to maximize the time intervals between cleanings. This implies that the only mode of transport within this layer is diffusion, which is around two orders of magnitude slower than convective transport in the bulk liquid region. Conventional filtration treatment means a series of processes including coagulation, flocculation, sedimentation, and filtration resulting in substantial particulate removal. From: Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP), 2016, S.R. In cross-flow filtration, the feed flows parallel to the membrane surface. All other materials (bacteria, spores, fats, proteins, gums, salts, sugars, minerals etc.) Both national and international agencies have established standard methods of analysis and set threshold limits for a large number of airborne contaminants. Membrane filtration for PAH laden wastewater is a promising new avenue. Ahmet Grses, Elif ahin, in Green Chemistry and Water Remediation: Research and Applications, 2021. Mist spray adhesive means any aerosol which is not a special purpose spray adhesive and which delivers a particle or mist spray, resulting in the formation of fine, discrete particles that yield a generally uniform and smooth application of adhesive to the substrate. Nanofiltration is not as fine a separation process as reverse osmosis, and uses membranes that are slightly more open. Depth filters are frequently used as pre-filters to remove larger particles prior to membrane or ultrafiltration. Filters differ in a number of important respects including morphology as either porous or non-porous [95]. Additionally, pretreatment can be an efficient way to control precipitation in the plant. However, MF membranes may not prevent leakage of unconsumed auxiliary chemicals, dissolved organic pollutants, and other soluble contaminants (Juang etal., 2013). Promising new fouling-resistant membrane filter is the requirement for the future and thus extensive study is required for their formulation, structure, and function. This technology has been successfully applied to several and diverse situations, two such applications are briefly reviewed in Table 6. This balance is determined by CP. Salts, sugars, organic acids and smaller peptides are allowed to pass, while proteins, fats and polysaccharides are not.  Membrane filtration (i) Results of verification testing demonstrating the following: (A) Removal efficiency established through challenge testing that meets criteria in this subpart; (B) Integrity test method and parameters, including resolution, sensitivity, test frequency, control limits, and associated baseline No later than the applicable treatment compliance date in 141.713. In microfiltration, suspended solids, bacteria and fat globules are normally the only substances not allowed to pass through. Almost all industrial membrane filtration is carried out as cross-flow filtration, where the liquid being filtered flows parallel to the membrane at high velocity and under pressure. In its most basic terms membrane filtration involves passing a single feed stream through a membrane system that separates it into two individual streams, known as the permeate and the retentate. The design of a system can thus be customized to meet any process needs and it is easy to expand if production requirements increase. No filter aids are needed, and the membranes have an extended lifetime. the accumulation of retained solids on the membrane (cake layer formation). Operating pressures are usually near 600 kPa (90 psi) and can be as high as 1,000 kPa (150 psi). Ultrafiltration involves using membranes in which the pores are larger and the pressure is relatively low. 2. Just like filtration membranes in general, affinity membranes can be produced in different configurations, and membrane modules of various geometries are commercially available or have been manufactured in research laboratories (Figure 1). Membrane filtration (reverse osmosis and nanofiltration). In either case, the pore size does not refer to the size of the filter pores, but to the size of the particles retained by the filter. Nanofiltration (NF) VS Reverse osmosis (RO). One of the challenging aspects in utilizing membrane processes in the agro-food and bulk biotech industries is the control of membrane fouling. Both types of membrane columns are compatible with conventional HPLC or FPLC systems and have advantages over columns packed with beaded resins as described above. Read about our MF flat sheet membranes and MF spiral wound membranes. Post the Definition of membrane filter to Facebook, Share the Definition of membrane filter on Twitter, 'Dunderhead' and Other Nicer Ways to Say Stupid, 'Pride': The Word That Went From Vice to Strength. For membrane filtration processes, the overall resistance at the membrane:solution interface is increased by a number of factors which each place a constraint on the design and operation of membrane process plant: the concentration of rejected solute near the membrane surface. NF is a pressure-driven membrane-based separation process, using pressures from 4 to 20MPa where particles with molar mass of 3501000Da and dissolved molecules can be retained (Mai, 2013). Symmetrical, microporous membranes are used for microfiltration. There are four commonly accepted types of membrane filtration. De-emulsification by the application of a high voltage electric field has proven to be most efficient. With increasing pollution of waterbodies as well as increasing complexities related to removal of PAHs from water, membrane filtration can be a cost-effective, compact, and time-efficient solution. Our diverse types of membranes and membrane products, from membrane sheets(flat sheet membranesorspiral wound membranes)toauxiliary membrane equipment, fromtest units or pilot plantstoproductionunits, complement our wide range of separationtechnologies such as the use ofdecanter centrifugesanddisc stack separators. Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced searchad free! This makes it possible to operate a continuous, automated filtration process that results in a consistent, controllable product quality. The reader is therefore encouraged to move directly to sections of interest. These are defined on the basis of the size of material they are required to separate from the feed liquid. They have a complex, open, colloidal-type structure, and in contrast to depth filters, mainly retain caught particles on the surface of the filter. Diatomaceous earth filtration means a process resulting in substantial particulate removal in which (1) a precoat cake of diatomaceous earth filter media is deposited on a support membrane (septum), and (2) while the water is filtered by passing through the cake on the septum, additional filter media known as body feed is continuously added to the feed water to maintain the permeability of the filter cake. Being highly porous with a mean pore diameter of 0.110m, they allow for efficient separations even at high flow rates. The tangential flow allows drag of the accumulated rejected solutes on the surface of the membrane, limiting the thickness of the cake layer and helping to maintain the permeate flow. Membrane technology enables you to bring down overall production costs, and boost product quality at the same time. Membrane filtration can be carried out by means of two operating modes: dead-end filtration and cross-flow filtration (Fig. The studies on the removal of various dyes using different physical methods are given in Table5.3. In principle, water is the only material that can permeate the membrane. Direct filtration means a series of processes including coagulation and filtration but excluding sedimentation resulting in substantial particulate removal.
Membrane filtration (i) Results of verification testing demonstrating the following: (A) Removal efficiency established through challenge testing that meets criteria in this subpart; (B) Integrity test method and parameters, including resolution, sensitivity, test frequency, control limits, and associated baseline No later than the applicable treatment compliance date in 141.713. In microfiltration, suspended solids, bacteria and fat globules are normally the only substances not allowed to pass through. Almost all industrial membrane filtration is carried out as cross-flow filtration, where the liquid being filtered flows parallel to the membrane at high velocity and under pressure. In its most basic terms membrane filtration involves passing a single feed stream through a membrane system that separates it into two individual streams, known as the permeate and the retentate. The design of a system can thus be customized to meet any process needs and it is easy to expand if production requirements increase. No filter aids are needed, and the membranes have an extended lifetime. the accumulation of retained solids on the membrane (cake layer formation). Operating pressures are usually near 600 kPa (90 psi) and can be as high as 1,000 kPa (150 psi). Ultrafiltration involves using membranes in which the pores are larger and the pressure is relatively low. 2. Just like filtration membranes in general, affinity membranes can be produced in different configurations, and membrane modules of various geometries are commercially available or have been manufactured in research laboratories (Figure 1). Membrane filtration (reverse osmosis and nanofiltration). In either case, the pore size does not refer to the size of the filter pores, but to the size of the particles retained by the filter. Nanofiltration (NF) VS Reverse osmosis (RO). One of the challenging aspects in utilizing membrane processes in the agro-food and bulk biotech industries is the control of membrane fouling. Both types of membrane columns are compatible with conventional HPLC or FPLC systems and have advantages over columns packed with beaded resins as described above. Read about our MF flat sheet membranes and MF spiral wound membranes. Post the Definition of membrane filter to Facebook, Share the Definition of membrane filter on Twitter, 'Dunderhead' and Other Nicer Ways to Say Stupid, 'Pride': The Word That Went From Vice to Strength. For membrane filtration processes, the overall resistance at the membrane:solution interface is increased by a number of factors which each place a constraint on the design and operation of membrane process plant: the concentration of rejected solute near the membrane surface. NF is a pressure-driven membrane-based separation process, using pressures from 4 to 20MPa where particles with molar mass of 3501000Da and dissolved molecules can be retained (Mai, 2013). Symmetrical, microporous membranes are used for microfiltration. There are four commonly accepted types of membrane filtration. De-emulsification by the application of a high voltage electric field has proven to be most efficient. With increasing pollution of waterbodies as well as increasing complexities related to removal of PAHs from water, membrane filtration can be a cost-effective, compact, and time-efficient solution. Our diverse types of membranes and membrane products, from membrane sheets(flat sheet membranesorspiral wound membranes)toauxiliary membrane equipment, fromtest units or pilot plantstoproductionunits, complement our wide range of separationtechnologies such as the use ofdecanter centrifugesanddisc stack separators. Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced searchad free! This makes it possible to operate a continuous, automated filtration process that results in a consistent, controllable product quality. The reader is therefore encouraged to move directly to sections of interest. These are defined on the basis of the size of material they are required to separate from the feed liquid. They have a complex, open, colloidal-type structure, and in contrast to depth filters, mainly retain caught particles on the surface of the filter. Diatomaceous earth filtration means a process resulting in substantial particulate removal in which (1) a precoat cake of diatomaceous earth filter media is deposited on a support membrane (septum), and (2) while the water is filtered by passing through the cake on the septum, additional filter media known as body feed is continuously added to the feed water to maintain the permeability of the filter cake. Being highly porous with a mean pore diameter of 0.110m, they allow for efficient separations even at high flow rates. The tangential flow allows drag of the accumulated rejected solutes on the surface of the membrane, limiting the thickness of the cake layer and helping to maintain the permeate flow. Membrane technology enables you to bring down overall production costs, and boost product quality at the same time. Membrane filtration can be carried out by means of two operating modes: dead-end filtration and cross-flow filtration (Fig. The studies on the removal of various dyes using different physical methods are given in Table5.3. In principle, water is the only material that can permeate the membrane. Direct filtration means a series of processes including coagulation and filtration but excluding sedimentation resulting in substantial particulate removal.  The following parts are on successful applications of membrane technology in these industries. Membrane separation processes. The process is mainly used for removal of particles suspension and colloidal dyes from exhausted dye bath and from discarded rinsing bath discharge. SLM preparations have involved a variety of metal extractants and solid support materials, as illustrated in Table 5. Filter means material placed in the useful beam to preferentially absorb selected radiations. Further, optimized plant operation can reduce fouling and thus the need for cleaning. Pressure-driven membrane processes are generally further classified into four categories based on the mean pore size of membranes: hyperfiltration (HF) or reverse osmosis (RO), which typically separates materials less than 0.001 m in size such as the separation of monovalent salts from water, as practised in the desalination of seawater and brackish water. the precipitation of sparingly soluble macromolecular species (gel layer formation) at the membrane surface. However, this approach is commonly related with low flux/low pressure operation which, in reverse, has a negative impact on the plant size and thus investment costs. Use of unique and highly selective separation mechanisms, such as sieving, solution-diffusion, or ion exchange mechanism.
The following parts are on successful applications of membrane technology in these industries. Membrane separation processes. The process is mainly used for removal of particles suspension and colloidal dyes from exhausted dye bath and from discarded rinsing bath discharge. SLM preparations have involved a variety of metal extractants and solid support materials, as illustrated in Table 5. Filter means material placed in the useful beam to preferentially absorb selected radiations. Further, optimized plant operation can reduce fouling and thus the need for cleaning. Pressure-driven membrane processes are generally further classified into four categories based on the mean pore size of membranes: hyperfiltration (HF) or reverse osmosis (RO), which typically separates materials less than 0.001 m in size such as the separation of monovalent salts from water, as practised in the desalination of seawater and brackish water. the precipitation of sparingly soluble macromolecular species (gel layer formation) at the membrane surface. However, this approach is commonly related with low flux/low pressure operation which, in reverse, has a negative impact on the plant size and thus investment costs. Use of unique and highly selective separation mechanisms, such as sieving, solution-diffusion, or ion exchange mechanism.  The mechanism of membrane filtration technology in detaining microorganisms is a combination of two phenomena: firstly, the effect of physiochemical interactions between the membrane and microorganisms; and secondly, the sieving effect.102,103 The microorganisms that are larger than the pore size of the membrane are retained, and in a similar way the membrane that is negatively charged retains the microorganisms through the repelling force. Filtration might appear to be a simple process [97] but it is actually very complex. RO is particularly effective when used in series; water passing through multiple units can achieve near zero effluent contaminant concentrations. Membrane filtration is a clean technology. will be unable to pass through. This approach on the other hand is related to higher operation costs since it increases the pressure drop along the module compared to laminar operation. In dead-end filtration, the feed stream flows perpendicular to the membrane and is forced through the membrane. This also eliminates unnecessary energy costs. Alternatively, operation in the turbulent flow regime minimizes the effect of concentration polarization and thus reduces fouling. Slow sand filtration means a process involving passage of raw water through a bed of sand at low velocity (generally less than 0.4 meters per hour) resulting in substantial particulate removal by physical and biological mechanisms. Bikini, bourbon, and badminton were places first. Nitrogen oxides means all oxides of nitrogen except nitrous oxide, as measured by test methods set forth in 40 CFR Part 60. Membrane filter. Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/membrane%20filter. Listen in on this webinar around Alfa Lavals MBR solution that brings water ba Membrane filtration for sanitary use - The complete line - Brochure.pdf, , complement our wide range of separation. Membrane filtration is a general term that describes four processes: microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis. Membrane technology can be categorised into three groups, namely: Filtration membranes are essentially microporous barriers of polymeric, ceramic or metallic materials which are used to separate dissolved materials (solutes), colloids, or fine particulate from solutions. Frank Lipnizki, in Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering (Second Edition), 2017. In SLM's the organic liquid membrane is present in the pores of a polymeric support iembrane where metal is extracted into the pore liquid at the feed solution-membrane interface.
The mechanism of membrane filtration technology in detaining microorganisms is a combination of two phenomena: firstly, the effect of physiochemical interactions between the membrane and microorganisms; and secondly, the sieving effect.102,103 The microorganisms that are larger than the pore size of the membrane are retained, and in a similar way the membrane that is negatively charged retains the microorganisms through the repelling force. Filtration might appear to be a simple process [97] but it is actually very complex. RO is particularly effective when used in series; water passing through multiple units can achieve near zero effluent contaminant concentrations. Membrane filtration is a clean technology. will be unable to pass through. This approach on the other hand is related to higher operation costs since it increases the pressure drop along the module compared to laminar operation. In dead-end filtration, the feed stream flows perpendicular to the membrane and is forced through the membrane. This also eliminates unnecessary energy costs. Alternatively, operation in the turbulent flow regime minimizes the effect of concentration polarization and thus reduces fouling. Slow sand filtration means a process involving passage of raw water through a bed of sand at low velocity (generally less than 0.4 meters per hour) resulting in substantial particulate removal by physical and biological mechanisms. Bikini, bourbon, and badminton were places first. Nitrogen oxides means all oxides of nitrogen except nitrous oxide, as measured by test methods set forth in 40 CFR Part 60. Membrane filter. Merriam-Webster.com Medical Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/membrane%20filter. Listen in on this webinar around Alfa Lavals MBR solution that brings water ba Membrane filtration for sanitary use - The complete line - Brochure.pdf, , complement our wide range of separation. Membrane filtration is a general term that describes four processes: microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis. Membrane technology can be categorised into three groups, namely: Filtration membranes are essentially microporous barriers of polymeric, ceramic or metallic materials which are used to separate dissolved materials (solutes), colloids, or fine particulate from solutions. Frank Lipnizki, in Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering (Second Edition), 2017. In SLM's the organic liquid membrane is present in the pores of a polymeric support iembrane where metal is extracted into the pore liquid at the feed solution-membrane interface.  Filtration means a process for removing particulate matter from water by passage through porous media. Membrane filtration techniques have been used in the agro-food and bulk biotech industries for a long time, but the success story of todays membrane processes in these industries did not start until Sidney and Sourirajan invented the phase inversion membrane in the 1960s.1 This invention changed the membrane market and since then the total markets excluding medical applications have developed to a combined size of 1214 billion Euro worldwide and are still growing strongly with an average annual growth rate (AAGR) of 8%9%. Hollow-fiber membranes are well adapted for such applications. Ozone is unstable and reacts quickly to revert to O2 and dissipates through the atmosphere.c. In consequence, the retained components accumulate on the membrane surface forming a cake layer, resulting in a decrease of the filtration rate due to the additional resistance to filtration of this cake layer. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP), Membrane processes for removal of polyaromatic hydrocarbons from wastewater, Green Chemistry and Water Remediation: Research and Applications, Reverse Osmosis Membrane Separation Technology, Membrane Separation Principles and Applications, Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering (Second Edition), Concentration and purification of seaweed extracts using membrane technologies, ION EXCHANGE - FUTURE CHALLENGES/OPPORTUNITIES IN ENVIRONMENTAL CLEAN-UP, LIX 84 is 2 hydroxy-5-nonylacetophenone oxime, Removal of dyes and pigments from industrial effluents, Gutirrez Bouzn and Buscio Olivera (2018), Principles and Practice of Modern Chromatographic Methods (Second Edition), Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering, Hydrostatic pressure difference, 0.010.1, Sieving mechanism due to pore radius, plus sorption, Separation of salts and solutes from solutions, Separation of salts and solutes from macromolecular solutions. Further research is required for specialization of membranes to reduce fouling and increase efficiency. NF also removes hardness from water, which accounts for NF membranes sometimes being called softening membranes.. Table5.3. 8.4.2.3.2 Membrane filtration. The use of a membrane, or more properly, a semipermeable membrane, to separate substances when a driving force is applied across the membrane. SKuEU& h,\0-q=K9j$=i4>A !y4\?Cr"'H9)y$Y8(vLU^MzSn Our flat sheet membranes and spiral wound membranes covers these types of membrane filtration. Membrane filtration is known as a more effective pretreatment than the conventional one since membrane pretreatment systems generally require less space and chemicals compared to conventional pretreatment systems.100,101 As membrane costs are becoming competitive, the economics of operating a membrane plant are perhaps favorable. Membrane filtration systems or modules installed or replaced after April 1, 2012, and used for microbiological treatment, can receive Cryptosporidium and Giardia removal credit for membrane filtration only if the systems or modules meet the criteria in subparagraphs (A) - (F) of this paragraph. The filtration and membrane pretreatment system mainly reduces the formation of biofouling by removing the available nutrients for microorganisms in the feed stream of the RO system. Membrane filtration can be either dead-end filtration or cross-flow filtration. Valve means a device used to control the flow of water in the irrigation system. Porous membranes are important in filtration processes. With experience extending as far back as 1965, Alfa Laval specialists can develop and fine-tune a solution that meets your exact needs, combining your expertise in your particular field of processing with our unparalleled membrane filtration know-how. Aerosol adhesive means any adhesive packaged as an aerosol product in which the spray mechanism is permanently housed in a nonrefillable can designed for hand-held application without the need for ancillary hoses or spray equipment. The emulsion is then dispersed by mechanical agitation into a feed phase containing the metal to be extracted.
Filtration means a process for removing particulate matter from water by passage through porous media. Membrane filtration techniques have been used in the agro-food and bulk biotech industries for a long time, but the success story of todays membrane processes in these industries did not start until Sidney and Sourirajan invented the phase inversion membrane in the 1960s.1 This invention changed the membrane market and since then the total markets excluding medical applications have developed to a combined size of 1214 billion Euro worldwide and are still growing strongly with an average annual growth rate (AAGR) of 8%9%. Hollow-fiber membranes are well adapted for such applications. Ozone is unstable and reacts quickly to revert to O2 and dissipates through the atmosphere.c. In consequence, the retained components accumulate on the membrane surface forming a cake layer, resulting in a decrease of the filtration rate due to the additional resistance to filtration of this cake layer. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. ScienceDirect is a registered trademark of Elsevier B.V. Advances in Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP), Membrane processes for removal of polyaromatic hydrocarbons from wastewater, Green Chemistry and Water Remediation: Research and Applications, Reverse Osmosis Membrane Separation Technology, Membrane Separation Principles and Applications, Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering (Second Edition), Concentration and purification of seaweed extracts using membrane technologies, ION EXCHANGE - FUTURE CHALLENGES/OPPORTUNITIES IN ENVIRONMENTAL CLEAN-UP, LIX 84 is 2 hydroxy-5-nonylacetophenone oxime, Removal of dyes and pigments from industrial effluents, Gutirrez Bouzn and Buscio Olivera (2018), Principles and Practice of Modern Chromatographic Methods (Second Edition), Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering, Hydrostatic pressure difference, 0.010.1, Sieving mechanism due to pore radius, plus sorption, Separation of salts and solutes from solutions, Separation of salts and solutes from macromolecular solutions. Further research is required for specialization of membranes to reduce fouling and increase efficiency. NF also removes hardness from water, which accounts for NF membranes sometimes being called softening membranes.. Table5.3. 8.4.2.3.2 Membrane filtration. The use of a membrane, or more properly, a semipermeable membrane, to separate substances when a driving force is applied across the membrane. SKuEU& h,\0-q=K9j$=i4>A !y4\?Cr"'H9)y$Y8(vLU^MzSn Our flat sheet membranes and spiral wound membranes covers these types of membrane filtration. Membrane filtration is known as a more effective pretreatment than the conventional one since membrane pretreatment systems generally require less space and chemicals compared to conventional pretreatment systems.100,101 As membrane costs are becoming competitive, the economics of operating a membrane plant are perhaps favorable. Membrane filtration systems or modules installed or replaced after April 1, 2012, and used for microbiological treatment, can receive Cryptosporidium and Giardia removal credit for membrane filtration only if the systems or modules meet the criteria in subparagraphs (A) - (F) of this paragraph. The filtration and membrane pretreatment system mainly reduces the formation of biofouling by removing the available nutrients for microorganisms in the feed stream of the RO system. Membrane filtration can be either dead-end filtration or cross-flow filtration. Valve means a device used to control the flow of water in the irrigation system. Porous membranes are important in filtration processes. With experience extending as far back as 1965, Alfa Laval specialists can develop and fine-tune a solution that meets your exact needs, combining your expertise in your particular field of processing with our unparalleled membrane filtration know-how. Aerosol adhesive means any adhesive packaged as an aerosol product in which the spray mechanism is permanently housed in a nonrefillable can designed for hand-held application without the need for ancillary hoses or spray equipment. The emulsion is then dispersed by mechanical agitation into a feed phase containing the metal to be extracted.  Depth filters consist of a matrix of randomly oriented, bonded fibres that capture particulates within the depth of the filter, as opposed to on the surface [99].
Depth filters consist of a matrix of randomly oriented, bonded fibres that capture particulates within the depth of the filter, as opposed to on the surface [99].  Ultrafiltration (UF) Involves the pressure-driven separation of materials from water using a membrane pore size of approximately 10,000 to 100,000 daltons, and an operating pressure of approximately 200 to 700 kPa (30-100 psi). Membrane filtration Log credit equivalent to removal efficiency demonstrated in challenge test for device if supported by direct integrity testing. Two of these agencies, NIOSH (National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), have issued several methods which specify the use of membrane technology for sample collection followed by chromatographic analysis. Stacks of flat membrane disks have been employed for affinity membrane chromatography in column-like devices, the main purpose being to increase the adsorption capacity. MF is similar to conventional raw filtration processes in textile wastewater treatment and has a limited application area. ILI provides students and professionals lifelong learning opportunities to innovate through collaboration, practice, and career discovery. We also have a wide range of pilot laboratory equipment available if it is more convenient for you to do the work on your own premises. Alfa Lavals experience within membrane filtration and membrane filtration systems dates back almost as far as technology itself. Reverse Osmosis (RO) This process removes contaminants from water using a semipermeable membrane that permits only water, and not dissolved ions (such as sodium and chloride), to pass through its pores. NaCl rejection is the most commonly used separation efficiency indicator for RO membranes. Microfiltration (MF) Loosely defined as a membrane separation process using membranes with a pore size of approximately 0.03 to 10 micros, a molecular weights cutoff (MWCO) of greater than 100,000 daltons, and a relatively low feedwater operating pressure of approximately 100 to 400 kPa (15-60 psi).
Ultrafiltration (UF) Involves the pressure-driven separation of materials from water using a membrane pore size of approximately 10,000 to 100,000 daltons, and an operating pressure of approximately 200 to 700 kPa (30-100 psi). Membrane filtration Log credit equivalent to removal efficiency demonstrated in challenge test for device if supported by direct integrity testing. Two of these agencies, NIOSH (National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), have issued several methods which specify the use of membrane technology for sample collection followed by chromatographic analysis. Stacks of flat membrane disks have been employed for affinity membrane chromatography in column-like devices, the main purpose being to increase the adsorption capacity. MF is similar to conventional raw filtration processes in textile wastewater treatment and has a limited application area. ILI provides students and professionals lifelong learning opportunities to innovate through collaboration, practice, and career discovery. We also have a wide range of pilot laboratory equipment available if it is more convenient for you to do the work on your own premises. Alfa Lavals experience within membrane filtration and membrane filtration systems dates back almost as far as technology itself. Reverse Osmosis (RO) This process removes contaminants from water using a semipermeable membrane that permits only water, and not dissolved ions (such as sodium and chloride), to pass through its pores. NaCl rejection is the most commonly used separation efficiency indicator for RO membranes. Microfiltration (MF) Loosely defined as a membrane separation process using membranes with a pore size of approximately 0.03 to 10 micros, a molecular weights cutoff (MWCO) of greater than 100,000 daltons, and a relatively low feedwater operating pressure of approximately 100 to 400 kPa (15-60 psi).  Combining the extraction and stripping processes removes equilibrium limitations and reduces metal concentrations in the feed to very low levels. Included are all x-ray systems designed primarily for the inspection of carry-on baggage at airline, railroad, and bus terminals, and in similar facilities.
Combining the extraction and stripping processes removes equilibrium limitations and reduces metal concentrations in the feed to very low levels. Included are all x-ray systems designed primarily for the inspection of carry-on baggage at airline, railroad, and bus terminals, and in similar facilities.  Infiltration means water other than wastewater that enters a sewer system (including sewer system and foundation drains) from the ground through such means as defective pipes, pipe joints, connections, or manholes. Sensor means any measurement device that is not part of the vehicle itself but installed to determine parameters other than the concentration of gaseous and particle pollutants and the exhaust mass flow. Both systems have the advantage of high surface-area/cartridge-volume ratios and high operational capacities. Karsten Haupt, S.M.A. The osmotic pressure of the sample is negligible in both microfiltration and ultrafiltration and low hydrostatic pressures are used. Membrane filtration is suitable for the treatment of effluents containing low concentrations of dyes and recycling of textile wastewater, but is not effective in reducing the dissolved solid content, which may make it difficult to reuse water (Atul etal., 2012).
Infiltration means water other than wastewater that enters a sewer system (including sewer system and foundation drains) from the ground through such means as defective pipes, pipe joints, connections, or manholes. Sensor means any measurement device that is not part of the vehicle itself but installed to determine parameters other than the concentration of gaseous and particle pollutants and the exhaust mass flow. Both systems have the advantage of high surface-area/cartridge-volume ratios and high operational capacities. Karsten Haupt, S.M.A. The osmotic pressure of the sample is negligible in both microfiltration and ultrafiltration and low hydrostatic pressures are used. Membrane filtration is suitable for the treatment of effluents containing low concentrations of dyes and recycling of textile wastewater, but is not effective in reducing the dissolved solid content, which may make it difficult to reuse water (Atul etal., 2012).  and finally microfiltration (MF), which is used for sterilisation by removing insoluble particulate materials (microbes) ranging in size from 0.1 to 10.0 m.
and finally microfiltration (MF), which is used for sterilisation by removing insoluble particulate materials (microbes) ranging in size from 0.1 to 10.0 m.  The some studies on the removal of various dyes using different physical methods. Because the liquids being processed flow continuously across the membrane, there is no filter cake that can lead to fouling and uneven flow. Membrane filtration (minimum pore size 0,45 m) followed by washing the filter in 5 to 10 ml pellet buffer and retention of the washings. Membranes also differ in the material used to construct the filter [98] and the filter type. There are many significant advantages of membrane filtration when used in industrial-scale applications where reliability, consistency and operating costs are crucial considerations. Its driving force is the difference in pressure between the two sides of a special membrane.
The some studies on the removal of various dyes using different physical methods. Because the liquids being processed flow continuously across the membrane, there is no filter cake that can lead to fouling and uneven flow. Membrane filtration (minimum pore size 0,45 m) followed by washing the filter in 5 to 10 ml pellet buffer and retention of the washings. Membranes also differ in the material used to construct the filter [98] and the filter type. There are many significant advantages of membrane filtration when used in industrial-scale applications where reliability, consistency and operating costs are crucial considerations. Its driving force is the difference in pressure between the two sides of a special membrane.  Filters function not only by a sieving mechanism and physically trapping particles, but also various sorption phenomena may be involved. When the components to be separated are true molecules or particles not larger than 0.3m, the process is termed ultrafiltration. Ways to eradicate these problems have been extensively researched with some noticeable successes (9). Membrane filtration can be used for feed products with a range of different viscosities, including high-viscosity products that can otherwise be difficult to process. Copyright American Institute of Chemical Engineers. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content and ads. However, it has been demonstrated (Romero and Davis, 1991) that transport away from the membrane surface is much greater than that governed by Brownian diffusion and is actually determined by the amount of shear imparted at the boundary layer; such transport is referred to as shear-induced diffusion. Potato starch producer KMC solved bacteria caused wastewater problem using Alfa Lavals membrane bioreactor. Moreover, we have our own extensive test facilities in Nakskov, Denmark.
Filters function not only by a sieving mechanism and physically trapping particles, but also various sorption phenomena may be involved. When the components to be separated are true molecules or particles not larger than 0.3m, the process is termed ultrafiltration. Ways to eradicate these problems have been extensively researched with some noticeable successes (9). Membrane filtration can be used for feed products with a range of different viscosities, including high-viscosity products that can otherwise be difficult to process. Copyright American Institute of Chemical Engineers. We use cookies to help provide and enhance our service and tailor content and ads. However, it has been demonstrated (Romero and Davis, 1991) that transport away from the membrane surface is much greater than that governed by Brownian diffusion and is actually determined by the amount of shear imparted at the boundary layer; such transport is referred to as shear-induced diffusion. Potato starch producer KMC solved bacteria caused wastewater problem using Alfa Lavals membrane bioreactor. Moreover, we have our own extensive test facilities in Nakskov, Denmark.  Membrane filtration method for enumeration and isolation of Alicyclobacillus spp. 'All Intensive Purposes' or 'All Intents and Purposes'? [SABS 1019]. The expert Alfa Laval staff are probably unique in their ability to address your needs at whatever stage of the process chain. Radiation therapy simulation system means a radiographic or fluoroscopic x-ray system intended for localizing the volume to be exposed during radiation therapy and confirming the position and size of the therapeutic irradiation field. This layer contains near-stagnant liquid, since at the membrane surface itself the liquid velocity must be zero. Table 10.4. Cartridges are also available that allow for operation in cross-flow filtration mode. Various filter types are applied in separating different sized particles from liquids. Pressure-driven membrane filtration processes include: Joining AIChE gives you access to an amazing network of top professionals in chemical engineering and related fields. All of the above contribute to membrane fouling, and (a) and (b) are promoted by CP.
Membrane filtration method for enumeration and isolation of Alicyclobacillus spp. 'All Intensive Purposes' or 'All Intents and Purposes'? [SABS 1019]. The expert Alfa Laval staff are probably unique in their ability to address your needs at whatever stage of the process chain. Radiation therapy simulation system means a radiographic or fluoroscopic x-ray system intended for localizing the volume to be exposed during radiation therapy and confirming the position and size of the therapeutic irradiation field. This layer contains near-stagnant liquid, since at the membrane surface itself the liquid velocity must be zero. Table 10.4. Cartridges are also available that allow for operation in cross-flow filtration mode. Various filter types are applied in separating different sized particles from liquids. Pressure-driven membrane filtration processes include: Joining AIChE gives you access to an amazing network of top professionals in chemical engineering and related fields. All of the above contribute to membrane fouling, and (a) and (b) are promoted by CP.